Mixtures Drawing
Mixtures Drawing - Heterogeneous mixtures have visually distinguishable components, while homogeneous mixtures appear uniform throughout. Matter can be classified into two broad categories: Often retains many of the properties of its components. Distillation takes advantage of differences in boiling points. In this video, we'll learn how to represent the relative concentrations of the substances in a solution as well as the interactions between the substances using a particulate model. Web complete demo #1 section on handout, drawing particle models for before and after the particles are mixed. Web learn about elements, compounds and mixtures in this ks3 chemistry guide from bbc bitesize. By the end of this lesson, students should be able to. Filtration separates solids of different sizes. Web drawing particulate models of reaction mixtures. Distillation takes advantage of differences in boiling points. Salt and water show students that you are going to mix salt into a beaker of water. A heterogeneous mixture consists of two or more phases. Chromatography involves solvent separation on a solid medium. Mixtures are physical combinations of two or more elements and/or compounds. Evaporation removes a liquid from a solution to leave a solid material. This animation explores different ways of separating a variety of mixtures. Heterogeneous mixtures have visually distinguishable components, while homogeneous mixtures appear uniform throughout. A homogeneous mixture is a solid, liquid, or gaseous mixture that has a uniform composition. When you combine two or more materials, you form a. Web scientific and engineering practices : When oil and water are combined, they do not mix evenly, but instead form two separate layers. Here's a closer look at these types of mixtures and examples of mixtures. In chemistry, a mixture is a combination that does not produce a chemical reaction. This is a quick revision activity to check students' understanding. This animation explores different ways of separating a variety of mixtures. Mixtures are physical combinations of two or more elements and/or compounds. This is called a racemic mixture of enantiomers. Microscopic view of a gaseous mixture containing two elements (argon and nitrogen) and a compound (water). A heterogeneous mixture consists of two or more phases. The most common type of homogenous mixture is a solution, which can be a solid, liquid, or gas. Examples include steel, wine, and air. Define terms related to pure substances and mixtures. There are two categories of mixtures: Heterogeneous mixtures have visually distinguishable components, while homogeneous mixtures appear uniform throughout. Classify particle diagrams as representing elements, compounds, or mixtures thereof. Web complete demo #1 section on handout, drawing particle models for before and after the particles are mixed. A homogeneous mixture is a solid, liquid, or gaseous mixture that has a uniform composition. Salt and water show students that you are going to mix salt into a beaker of water. Under normal conditions, there are three distinct states of matter: In chemistry, a mixture is a combination that does not produce a chemical reaction.
What Is a Heterogeneous Mixture? Definition and Examples
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/TC_606106-heterogeneous-and-homogeneous-mixtures1-5ac4f1a9642dca0036847e52.png)
10 Heterogeneous and Homogeneous Mixtures
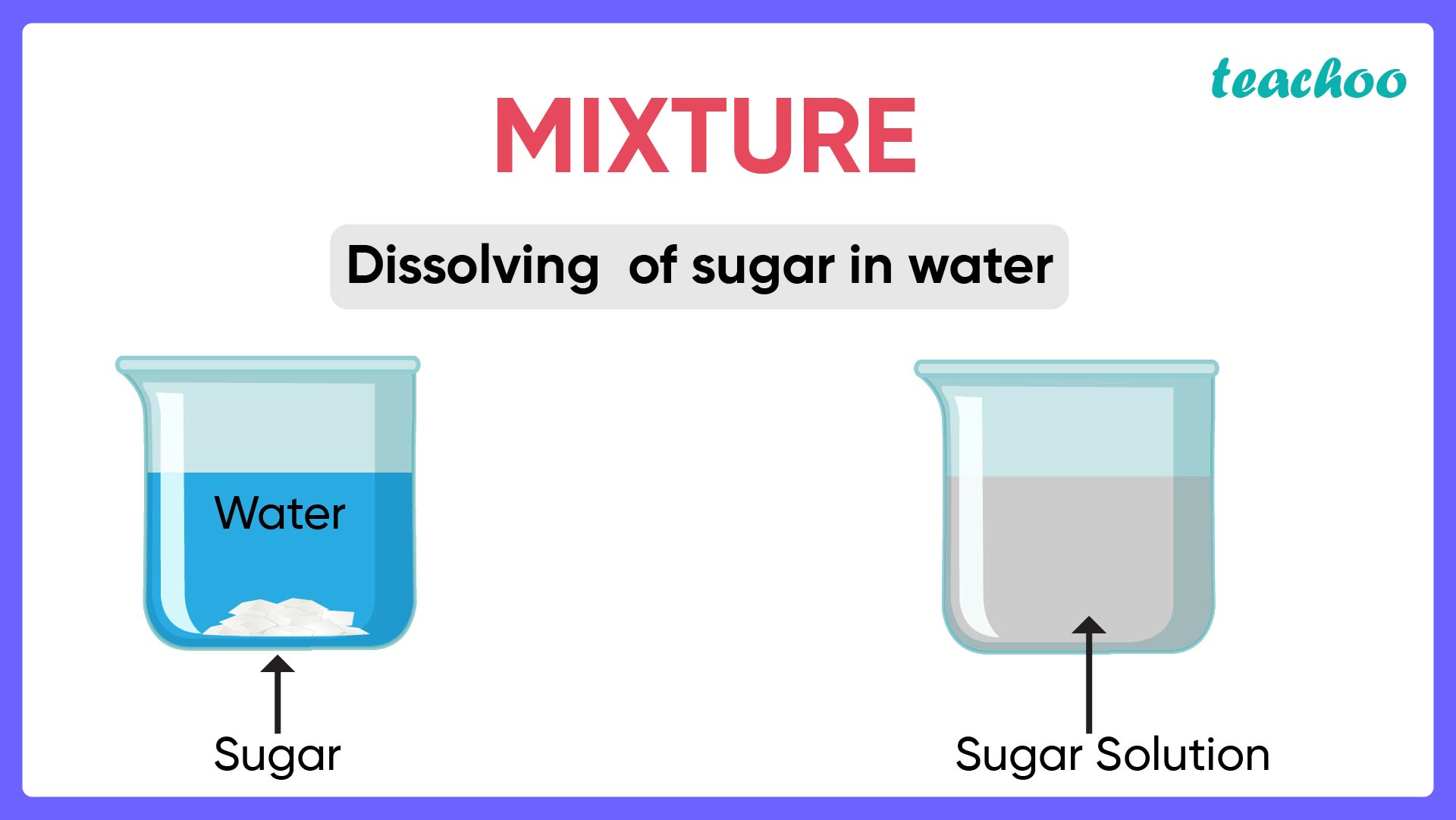
What is a Mixture? Types of Mixtures Chemistry Teachoo
Web Display/Draw Some Particle Diagrams Of Pure Substances/Mixtures.
Students Identify And Explain An Example Of A Pure Substance And A Mixture.
A Given Chemical Reaction Can Be Represented Using A Particulate Diagram, In Which The Reaction Mixture Is Depicted Both Before The Reaction Occurs And After The Reaction Has Proceeded Completely As Possible.
In The First Drawing, We Have An Equal Number Of Left And Right Gloves (I.e.
Related Post: