Smooth Muscle Drawing
Smooth Muscle Drawing - Smooth muscle longitudinal section labeled. Web structure and function. Explain how smooth muscles differ from skeletal and cardiac muscles. Smooth muscle cells (orange with purple nuclei) are embedded in the extracellular matrix, which is largely made of collagen and elastin fibers (green). Smooth muscle differs from skeletal muscle in function. Smooth muscle is a type of muscle tissue which is used by various systems to apply pressure to vessels and organs. How to draw smooth muscle cell diagram | how to draw smooth muscle cell. Schematic drawing of a longitudinal section of a bundle of smooth muscle cells. Compared with relaxed muscle, the activated muscle has more short (<0.3 μm) filaments and less long (>0.3 μm) filaments. By the end of this section, you will be able to: Web explain how smooth muscle works with internal organs and passageways through the body. Unlike skeletal muscle, smooth muscle is capable of maintaining tone for extended periods and often contracts involuntarily. These muscles are found in almost all organs in the form of bundles or sheaths. Web structure and function. Fibers of smooth muscle group in branching bundles, which allows. Fibers of smooth muscle group in branching bundles, which allows for cells to contract much stronger than those of striated musculature. How to draw a muscle. Unlike skeletal muscle, smooth muscle is capable of maintaining tone for extended periods and often contracts involuntarily. You will also find a details description of the smooth muscle fibers compared to cardiac and skeletal. Smooth muscle histology slide identification. How to draw smooth muscle diagram | how to draw smooth muscle | how to draw smooth muscle tissuehello friends in this video i tell you about how to dr. Explain how smooth muscles differ from skeletal and cardiac muscles. Fibers of smooth muscle group in branching bundles, which allows for cells to contract much. Schematic drawing of a longitudinal section of a bundle of smooth muscle cells. Web explain how smooth muscle works with internal organs and passageways through the body. They form the major contractile tissues of various organs. Unlike skeletal muscle, smooth muscle is capable of maintaining tone for extended periods and often contracts involuntarily. Web smooth muscle fibers are smaller than those of striated muscle. Smooth muscle location and their histological features. Unlike cardiac and skeletal muscle cells, smooth muscle cells do not exhibit striations since their actin and myosin (thin and thick) protein filaments are not organized as sarcomeres. Explain how smooth muscles differ from skeletal and cardiac muscles. It’s important to remember that smooth muscle cells can align with their long axis parallel and staggered longitudinally so that the white central portion of one cell lies next to the tapered end of another. Smooth muscle is a type of muscle tissue which is used by various systems to apply pressure to vessels and organs. Smooth muscle differs from skeletal muscle in function. Smooth muscle is composed of sheets or strands of smooth muscle cells. Web table of contents. Fibers of smooth muscle group in branching bundles, which allows for cells to contract much stronger than those of striated musculature. How to draw a muscle. 80k views 2 years ago class 9 diagram.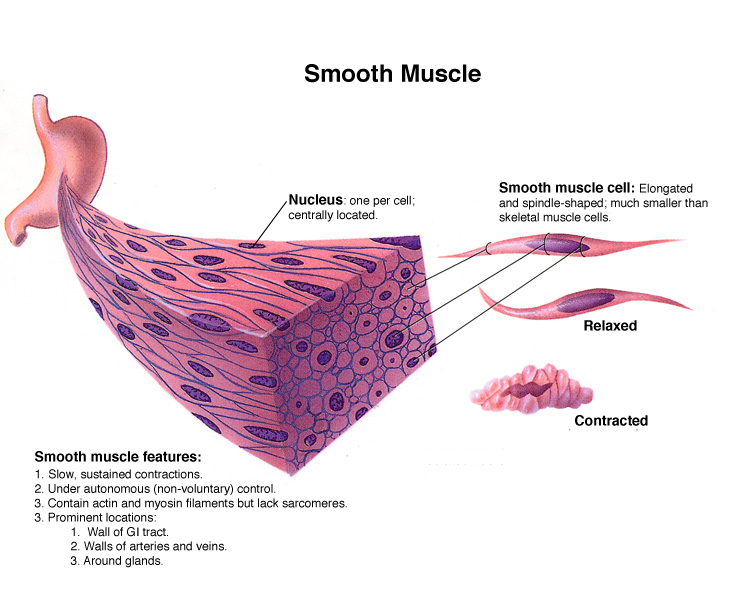
Honors Anatomy and Physiology Smooth and Skeletal Muscle

Smooth Muscle Diagram Labeled Draw Well Labelled Diagrams Of Various

Smooth Muscle Diagram Labeled Class 9 Musclenerve Mus vrogue.co
Explain How Smooth Muscles Differ From Skeletal And Cardiac Muscles.
Compared With Relaxed Muscle, The Activated Muscle Has More Short (<0.3 Μm) Filaments And Less Long (>0.3 Μm) Filaments.
Smooth Muscle Longitudinal Section Labeled.
Muscles Work In Pairs, With One Muscle Contracting While The Other Relaxes.
Related Post: