Plasma Membrane Drawing Labeled
Plasma Membrane Drawing Labeled - Structure of the plant cell (plasma) membrane. The plasma membrane is selectively permeable. The plasma membrane, which is also called the cell membrane, has many functions, but the most basic one is to define the borders of the cell and keep the cell functional. Web plant cell (plasma) membrane. Use arrows to show the relevant gradients and the activity of the following membrane proteins: The membrane is partially made up of molecules called phospholipids, which spontaneously arrange themselves into a double layer with hydrophilic (“water loving”) heads on the outside and hydrophobic (“water hating”) tails on the inside. The plasma membrane, which is also called the cell membrane, has many functions, but the most basic one is to define the borders of the cell and keep the cell functional. Web plasma membrane structure. Web the addition of new membrane to the plasma membrane is usually coupled with endocytosis so that the cell is not constantly enlarging. The plasma membrane mediates cellular processes by regulating the materials that enter and exit. The plasma membrane is selectively permeable. Web a diagram of a plasma membrane shows a phospholipid bilayer with 3 proteins embedded in the bilayer. Web bilayer structure of the plasma membrane. Web plant cell (plasma) membrane. This cell membrane provides a protective barrier around the cell and regulates which materials can pass in or out. The phospholipid bilayer with hydrophobic 'tails' and hydrophilic 'heads' of the. Structure of the plant cell (plasma) membrane. (1) a pump that exports protons; Web 62k views 11 years ago. Functions of the plant cell (plasma) membrane. The membrane is partially made up of molecules called phospholipids, which spontaneously arrange themselves into a double layer with hydrophilic (“water loving”) heads on the outside and hydrophobic (“water hating”) tails on the inside. Describe the structure of cell membranes. Web the structure of a plasma membrane. Exocytosis is much like endocytosis in reverse. Its facts, analogy, composition, location, &. (1) a pump that exports protons; Its facts, analogy, composition, location, & functions described using examples & labeled picture. The membrane also protects and supports the cell and controls everything that enters and leaves it. Material destined for export is. Exocytosis is much like endocytosis in reverse. Identify components of the cell membrane, including phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates. Use arrows to show the relevant gradients and the activity of the following membrane proteins: This figure shows how proteins and phospholipids are organized into a membrane. The plasma membrane protects intracellular components from the extracellular environment. The plasma membrane, which is also called the cell membrane, has many functions, but the most basic one is to define the borders of the cell and keep the cell functional. Web plant cell (plasma) membrane. The membrane is partially made up of molecules called phospholipids, which spontaneously arrange themselves into a double layer with hydrophilic (“water loving”) heads on the outside and hydrophobic (“water hating”) tails on the inside. Describe the structure of cell membranes. When drawing and labeling a diagram of the plasma membrane you should be sure to include: Web the plasma membrane is a structure that forms a barrier between the cytoplasm inside the cell and the environment outside the cell. The 3 proteins have lines with the label integral membrane proteins.
Cell Membrane Labeled Plasma membrane, Cell membrane, Cell membrane
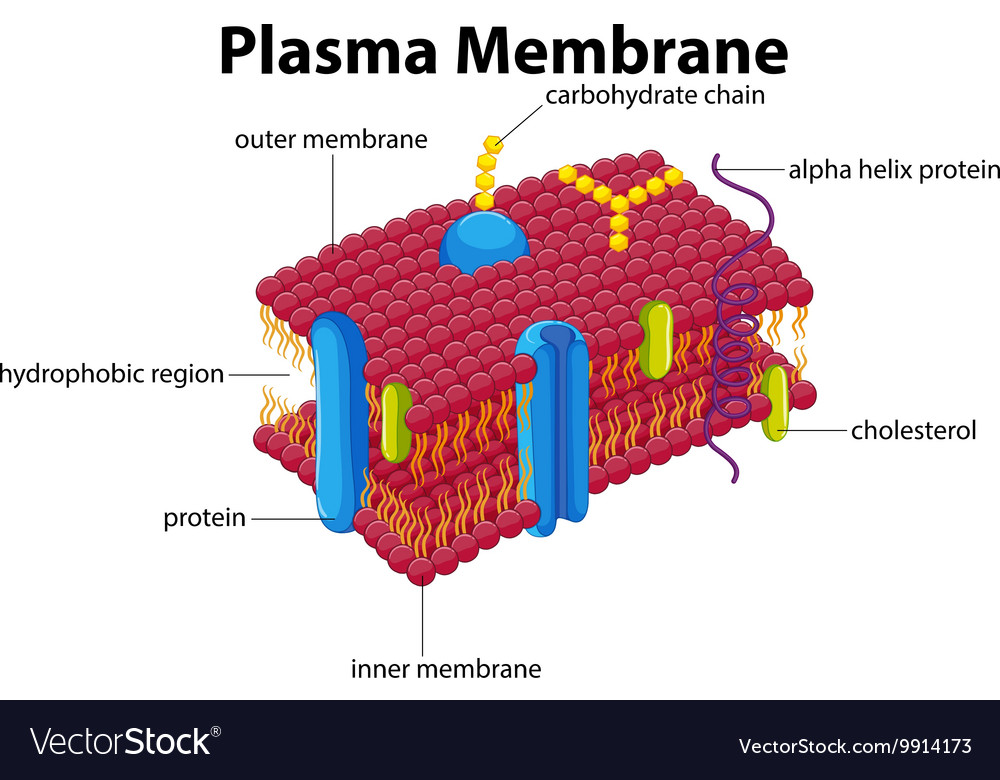
Diagram with plasma membrane Royalty Free Vector Image

Cell Membrane Diagram Easy to draw cell membrane YouTube
Web What Is A Cell (Plasma) Membrane And What It Does In A Cell:
Web Bilayer Structure Of The Plasma Membrane.
Web The Addition Of New Membrane To The Plasma Membrane Is Usually Coupled With Endocytosis So That The Cell Is Not Constantly Enlarging.
Web Image Of The Plasma Membrane, Showing The Phospholipid Bilayer With Peripheral And Integral Membrane Proteins, Glycoproteins (Proteins With A Carbohydrate Attached), Glycolipids (Lipids With A Carbohydrate Attached), And Cholesterol Molecules.
Related Post: