Phospholipid Drawing
Phospholipid Drawing - Web a diagram of a plasma membrane shows a phospholipid bilayer with 3 proteins embedded in the bilayer. The 3 proteins have lines with the label integral membrane proteins. A phospholipid is a type of lipid molecule that is the main component of the cell membrane. There are two important parts of a phospholipid: Phospholipids form the basic structure of the membrane (the phospholipid bilayer) they are formed by a hydrophilic phosphate head bonding with two hydrophobic hydrocarbon (fatty acid) tails. Created by william tsai.watch the next lesson: Web the parts of a phospholipid molecule. The vital role of phospholipids. We sometimes talk about fat as if it were a malevolent substance bent on our dietary destruction. The head and the two tails. The vital role of phospholipids. The hydrophobic tails face inward towards one another, and the hydrophilic heads face outwards. In sketching cell membrane structures, a phospholipid molecule is often represented by an icon like the above with the top part. Web each phospholipid is amphipathic, with two hydrophobic tails and a hydrophilic head. And all of this is held together. Web learn about the detailed structure of phospholipids in the cell membrane. Web each phospholipid is amphipathic, with two hydrophobic tails and a hydrophilic head. Stearic acid is shown as the fatty acid, but there are many variations in the fatty acids. Overview of lipids, covering fats and oils, saturated and unsaturated fats, triglycerides (triacylglycerols), phospholipids, and steroids. Make certain. Identify the polar (hydrophilic) and nonpolar (hydrophobic) regions of a phospholipid. Describe membrane components and how they are arranged. Make certain that you can define, and use in context, the key terms below. This phospholipid has nitrogen containing choline in its phosphorylated component. The head and the two tails. Created by william tsai.watch the next lesson: Stearic acid is shown as the fatty acid, but there are many variations in the fatty acids. As phospholipids have a hydrophobic and hydrophilic part they are known as amphipathic. 1k views 2 years ago a level biology. A phospholipid is an amphipathic molecule which means it has both a hydrophobic and a hydrophilic component. Web structure of a phospholipid molecule. The head and the two tails. Web each phospholipid is amphipathic, with two hydrophobic tails and a hydrophilic head. This phospholipid contains hexahydric alcohol called inositol in its phosphorylated component. Web lipids (article) | macromolecules | khan academy. Overview of lipids, covering fats and oils, saturated and unsaturated fats, triglycerides (triacylglycerols), phospholipids, and steroids. The vital role of phospholipids. And all of this is held together by glycerol backbone. Web this sketch of a phospholipid molecule shows two fatty acids and a phosphate group attached to a glycerol backbone. Components of the plasma membrane. Web the phospholipid bilayer consists of two adjacent sheets of phospholipids, arranged tail to tail.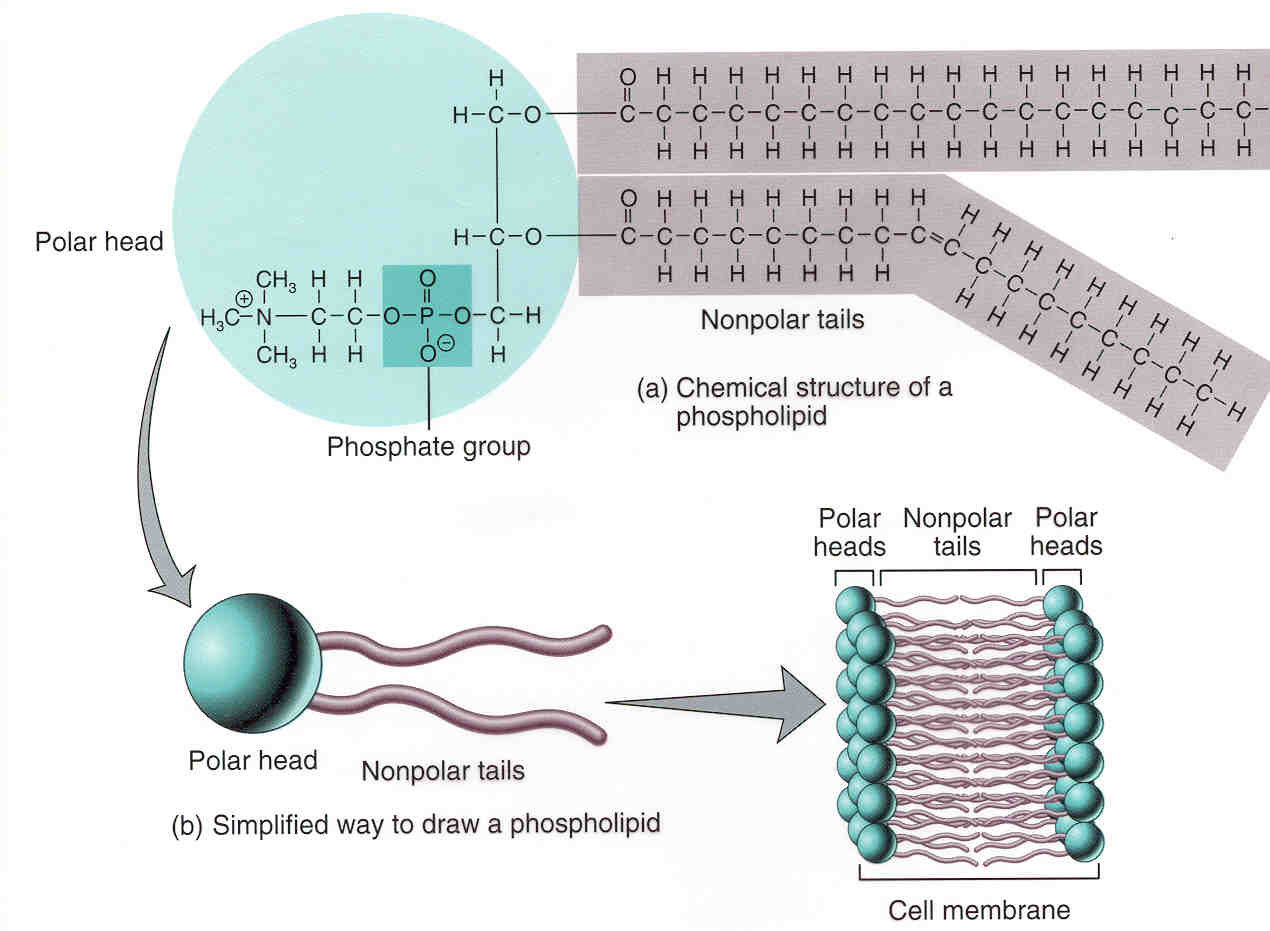
Phospholipid Bilayer Introduction, Structure and Functions

How to Draw a Phospholipid Bilayer YouTube
14.3 Phospholipids in Cell Membranes Chemistry LibreTexts
Each Phospholipid Is Made Up Of Two Fatty Acids, A Phosphate Group, And A Glycerol Molecule.
This Phospholipid Has Nitrogen Containing Choline In Its Phosphorylated Component.
Phospholipids Form The Basic Structure Of The Membrane (The Phospholipid Bilayer) They Are Formed By A Hydrophilic Phosphate Head Bonding With Two Hydrophobic Hydrocarbon (Fatty Acid) Tails.
The Polar Heads Contact The Fluid Inside And Outside Of The Cell.
Related Post: