Nuclear Membrane Drawing
Nuclear Membrane Drawing - Web the nuclear envelope, also called the nuclear membrane, is the outer covering of the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The nuclear envelope partitions nuclear contents from the cytoplasm and controls access of cytoplasmic proteins to the genome ( hetzer, 2010;. Mitosis ends with telophase, or the stage at which the chromosomes reach the poles. Web a crucial part of mitosis involves breaking down the nuclear membrane that surrounds the cell’s dna so that the dna can be replicated and separated into new cells. You may see the double membrane of the nuclear envelope. Web survey the slide to find a cell in each phase of mitosis. Both the inner and outer membranes of the nuclear. Some chromosomes have sections of dna that encode. The nuclear membrane then reforms, and the. These two cells will now enter meiosis ll. The nuclear membrane is a double layer that encloses the cell’s nucleus, where the chromosomes reside. The inner nuclear membrane (inm) and outer nuclear membrane (onm)), nuclear pore. Animal cells are eukaryotic and thus have a nucleus and a nuclear membrane. The nuclear membrane, also called the nuclear envelope, is a. Web zoom in on the micrograph; Web diagram of the parts of the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. Web zoom in on the micrograph; These two cells will now enter meiosis ll. Web redraw the nuclear membrane around the chromosomes and draw a nucleolus inside of each nucleus. The function of the animal. An inner nuclear membrane and an outer nuclear membrane. Some chromosomes have sections of dna that encode. These two cells will now enter meiosis ll. The nuclear membrane serves to separate. Draw a cell for each phase below. The nuclear envelope, also known as the nuclear membrane, is made up of two lipid bilayer membranes that in eukaryotic cells surround the nucleus, which encloses the genetic material. The nuclear membrane is a double layer that encloses the cell’s nucleus, where the chromosomes reside. Web zoom in on the micrograph; Mitosis ends with telophase, or the stage at which the chromosomes reach the poles. You may see the double membrane of the nuclear envelope. The space between the membra… Draw a cell for each phase below. The nuclear envelope partitions nuclear contents from the cytoplasm and controls access of cytoplasmic proteins to the genome ( hetzer, 2010;. Web a crucial part of mitosis involves breaking down the nuclear membrane that surrounds the cell’s dna so that the dna can be replicated and separated into new cells. Drawing the cell membrane and nucleus. The cell nucleus is the most noticeable organelle within the eukaryotic cell, and perhaps the most important and defining feature. You can also make out ribosomes (small granules) bound to both the rer and the outer. See nuclear membrane stock video clips. Animal cells are eukaryotic and thus have a nucleus and a nuclear membrane. The cell membrane of an animal cell is. The inner nuclear membrane (inm) and outer nuclear membrane (onm)), nuclear pore complexes.
Nuclear Membrane Definition (v1) by National Human Genome Research
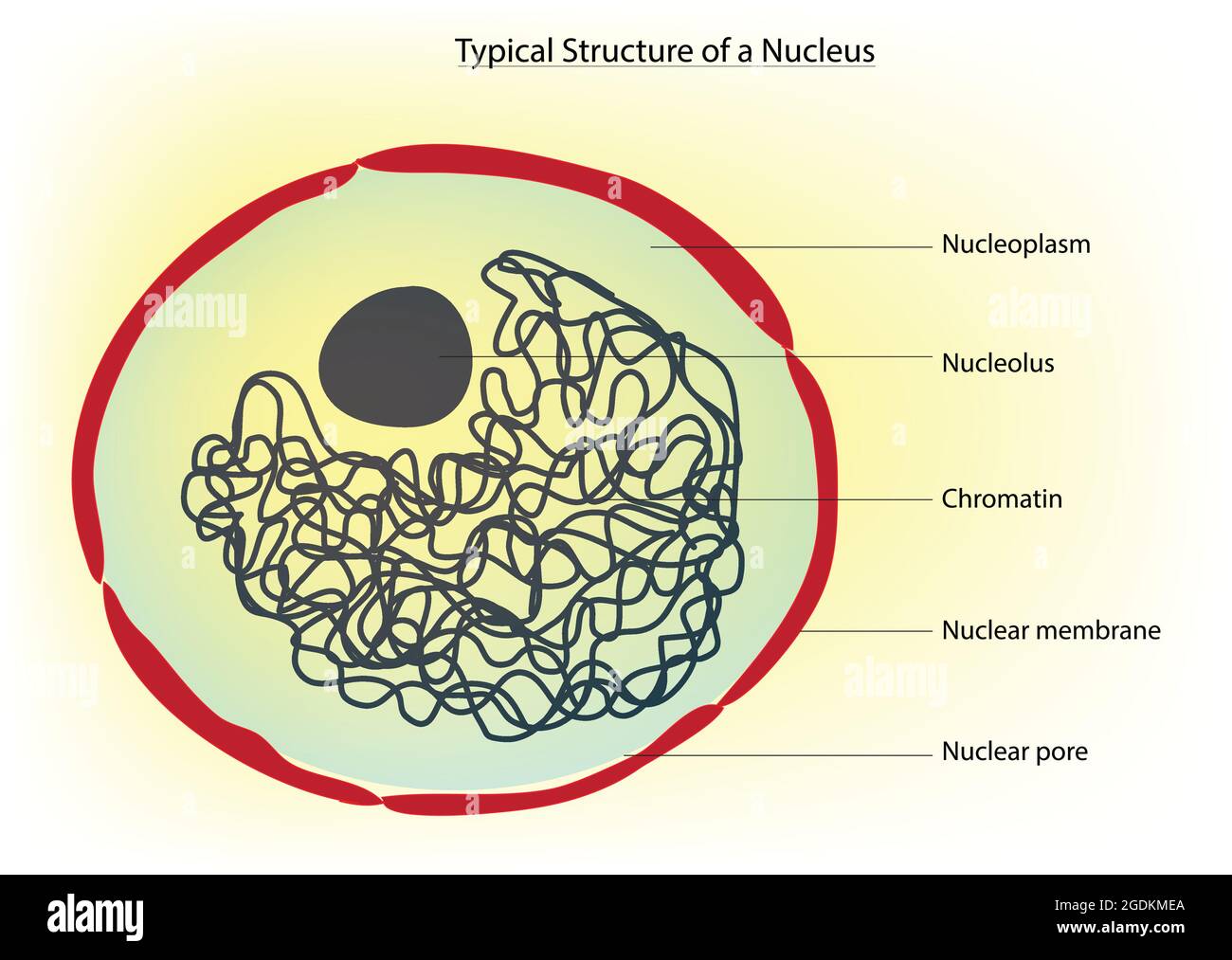
nucleus, membranebound organelle that contains the cell's chromosomes
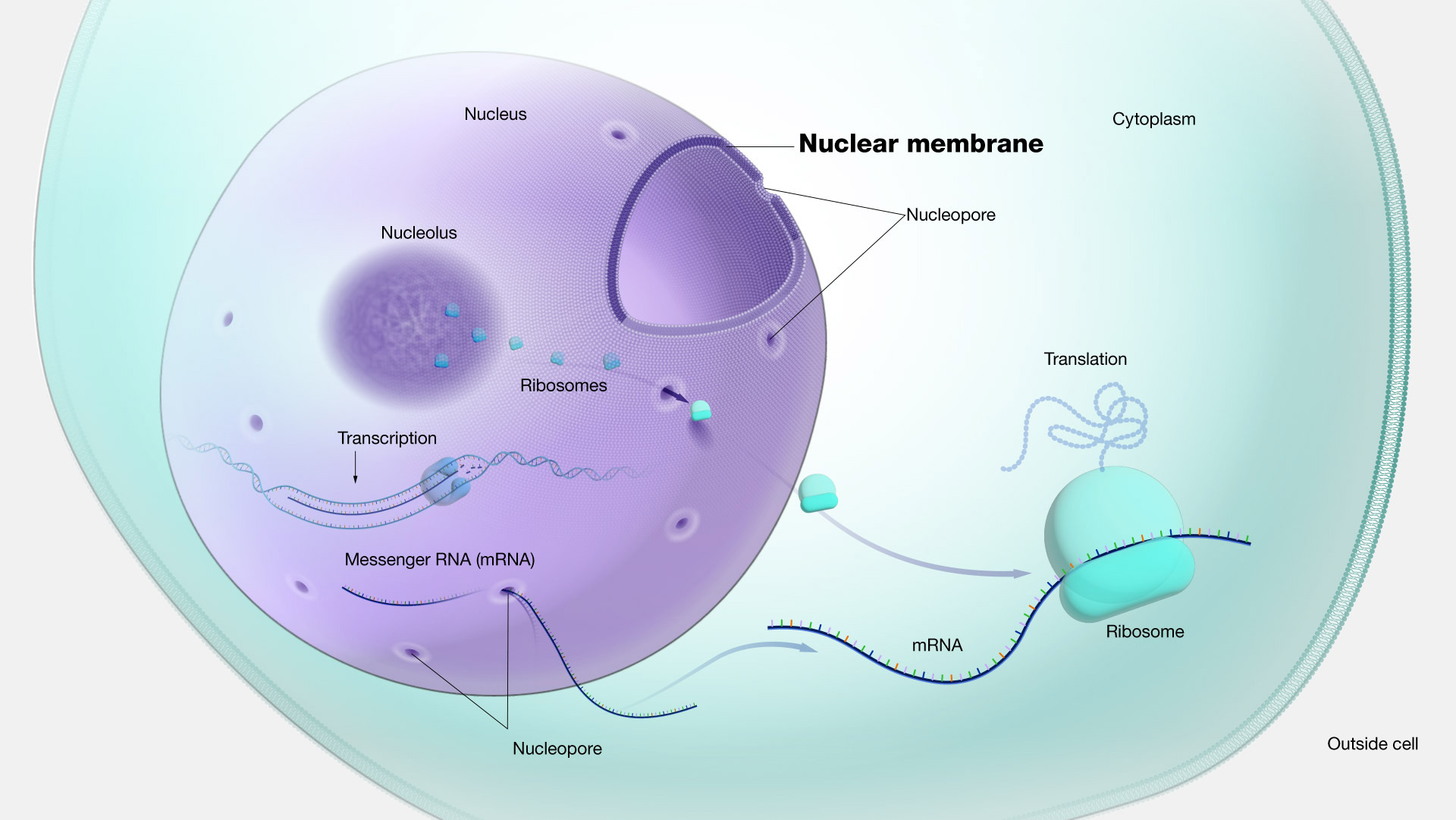
Nuclear Membrane
Some Chromosomes Have Sections Of Dna That Encode.
The Dna Is Uncondensed And In The Form Of Chromatin.
The Nuclear Envelope Consists Of Two Lipid Bilayer Membranes:
The Nuclear Membrane Serves To Separate.
Related Post: