How To Draw The Molecular Orbital Diagram
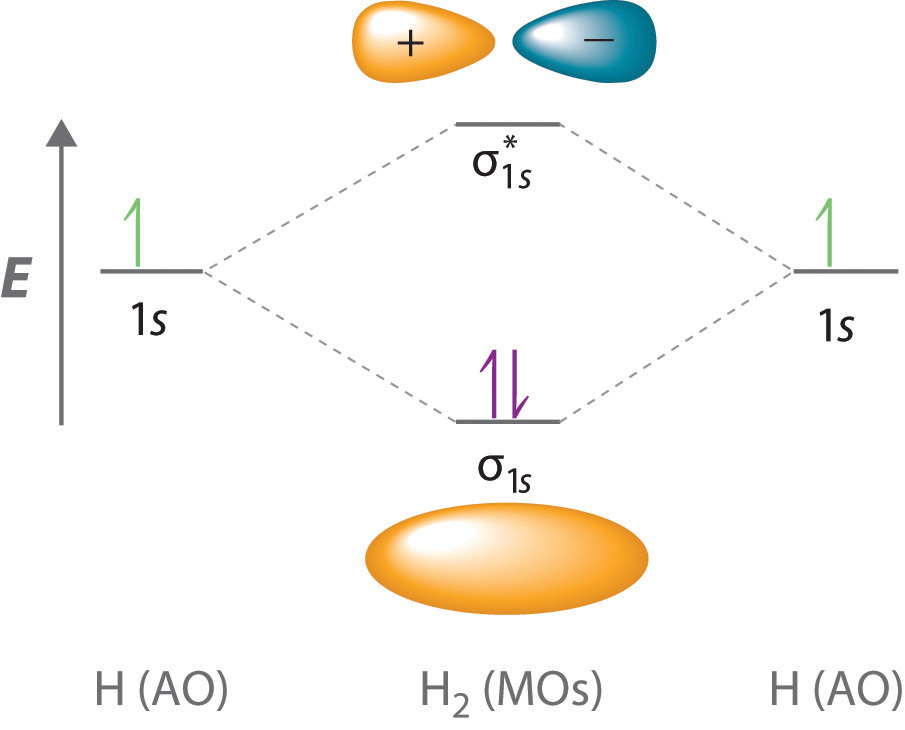
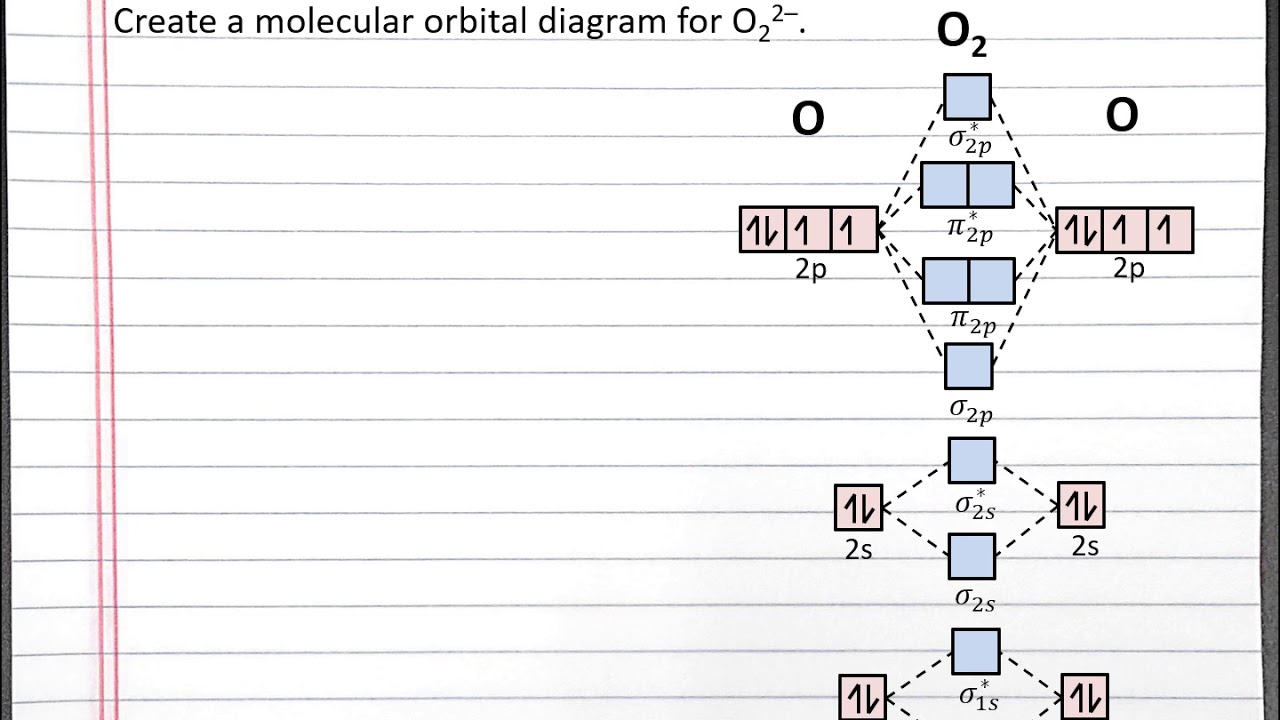
How To Draw The Molecular Orbital Diagram - How to draw a molecular orbital diagram. Valence bond theory is able to explain many aspects of bonding, but not all. Web how to draw molecular orbital diagrams for conjugated systems. Mo diagrams can be used to determine a molecule’s magnetic properties and how they change with ionisation. To complement this theory, we use another called the molecular orbital (mo) theory. In the third column, draw the atomic diagram for your second element. Web molecular orbital diagrams, bond order, and number of unpaired electrons draw the molecular orbital diagram for the oxygen molecule, o 2. It is analogous to the atomic orbital energy diagram (which goes 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s.). This gives you the total number of electrons you will have to distribute among the molecular orbitals you form. Learn to draw molecular orbital electron configuration energy diagrams. I will use oxygen ( o2(g)) as an example. Solution we draw a molecular orbital energy diagram similar to that shown in figure 8.37. It describes the formation of bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals from the combination of. Valence bond theory is able to explain many aspects of bonding, but not all. The bond order of the boron cation is. Draw out the orbitals of the central atoms. Molecular orbital diagrams are diagrams of molecular orbital (mo) energy levels, shown as short horizontal lines in the center, flanked by constituent atomic orbital (ao) energy levels for comparison, with the energy levels increasing from the. In the third column, draw the atomic diagram for your second element. Web this chemistry video. General chemistry supplement (eames) molecular orbital theory. Web the objective of this wiki is to provide readers with the fundamental steps in constructing simple homonuclear and heteronuclear diatomic molecular orbital diagrams. Web drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. Mo diagrams can be used to determine a molecule’s magnetic properties and how they change with. Determine point group of molecule (if linear, use d. Web to understand the bonding of a diatomic molecule, a molecular orbital diagram is used. Web the objective of this wiki is to provide readers with the fundamental steps in constructing simple homonuclear and heteronuclear diatomic molecular orbital diagrams. Determine the atomic orbitals of your atoms. Learn to draw molecular orbital electron configuration energy diagrams. Web construct a molecular orbital diagram of the kind shown in this lesson for a simple diatomic molecule, and indicate whether the molecule or its positive and negative ions should be stable. Construct mo diagrams for simple diatomic molecules and/or compounds. Web drawing molecular orbital diagrams determine how many valence electrons you have on each atom (you can ignore the core electrons as core orbitals contribute little to molecular orbitals). Reading and writing mo diagrams. Determine the total number of valence electrons in the he 2 2 + ion. The middle of the diagram is just the molecular orbital energy diagram. Determine the irreducible representation of the orbitals of the central atoms. With oxygen, you know that the atomic orbital potential energies go in the following order: Mo diagrams can be used to determine a molecule’s magnetic properties and how they change with ionisation. Web construct a molecular orbital diagram of the kind shown in this lesson for a simple diatomic molecule, and indicate whether the molecule or its positive and negative ions should be stable. Web molecular orbital diagrams are complex, involving two additional orbitals, electronegativity, atomic symmetries and atomic energies.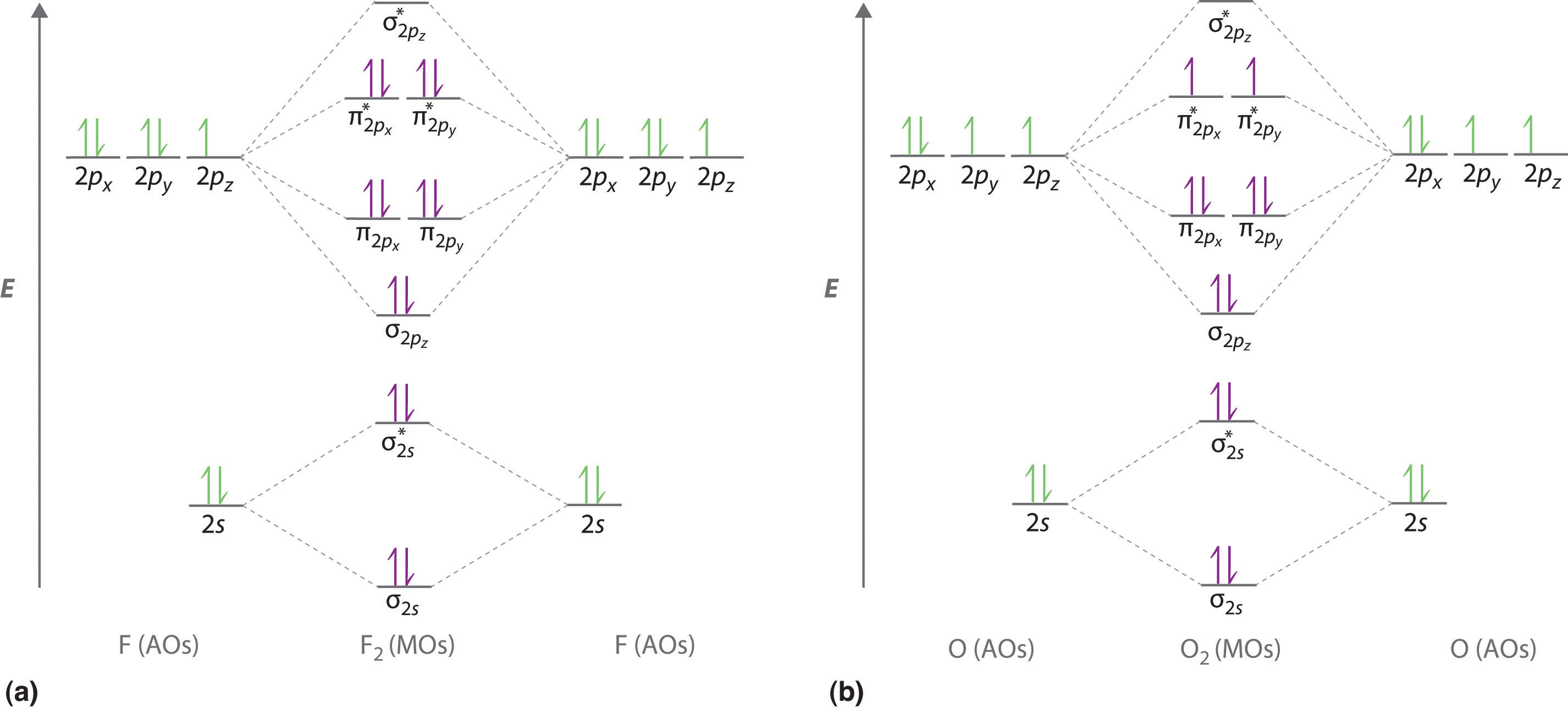
Molecular Orbital Theory Chemistry LibreTexts
4.9 Molecular Orbitals Chemistry LibreTexts
How To Draw A Molecular Orbital Diagram Elevatorunion6
Although More Complex, These Diagrams Reveal A More Realistic Case For Bonding, Allowing Electrons To Travel About A Molecule, Rather Than In Between One.
Draw Out The Possible Bonding Interaction Of The Orbitals From The Peripheral Atoms.
V 1S << V 2S < V 2P.
They Also Demonstrate The Molecule’s Bond Order, Or How Many Bonds Are Shared Between The Two Atoms.
Related Post: