How To Draw Supply Curve
How To Draw Supply Curve - In the graph, we see two axes. Aggregate supply is the total quantity of output firms will produce and sell—in other words, the real gdp. This causes a higher or lower quantity to be supplied at a given price. Supply and quantity supplied, supply schedule and supply curve, movement along and shift in a supply curve. A quick and comprehensive intro to supply and demand. Supply curves relate prices and quantities supplied assuming no other factors change. The supply curve may shift to the left. This video graphs all three types of linear supply curves: A higher price causes an extension along the supply curve (more is supplied) a lower price causes a contraction along the supply curve (less is supplied) supply shifts to the left. Web in most cases, the supply curve is drawn as a slope rising upward from left to right, since product price and quantity supplied are directly related (i.e., as the price of a commodity increases in the market, the amount supplied increases). The supply curve may shift to the left. Numerical methods to derive the supply curve. In the graph, we see two axes. Web the logic of the model of demand and supply is simple. This video graphs all three types of linear supply curves: Web the supply curve is a graphical representation of the quantity of goods or services that a supplier willingly offers at any given price. In this video, we use a supply schedule to demonstrate how to properly draw a. Graph functions, plot points, visualize algebraic equations, add sliders, animate graphs, and more. This represents how supply works. The supply curve. The upward slope of the supply curve illustrates the law of supply—that a higher price leads to a higher quantity supplied, and vice versa. The supply curve shows the quantities that sellers will offer for sale at each price during that same period. Web a linear supply curve can be plotted using a simple equation p. This is a very. We shall explain the concepts of supply, demand, and market. The supply curve can be seen as a visual demonstration of how. Supply and quantity supplied, supply schedule and supply curve, movement along and shift in a supply curve. Web the supply curve is a graphical representation of the quantity of goods or services that a supplier willingly offers at any given price. The supply curve may shift to the left. Numerical methods to derive the supply curve. Web explore math with our beautiful, free online graphing calculator. Changes in production cost and related factors can cause an entire supply curve to shift right or left. The horizontal axis represents q (quantity) and the vertical axis represents p (price). This video graphs all three types of linear supply curves: This causes a higher or lower quantity to be supplied at a given price. The upward slope of the supply curve illustrates the law of supply—that a higher price leads to a higher quantity supplied, and vice versa. P = 30+0.5 (qs) inverse supply curve. It follows that a change in any of those variables will cause a change in supply, which is a shift in the supply curve. This represents how supply works. In this diagram the supply curve shifts to the left.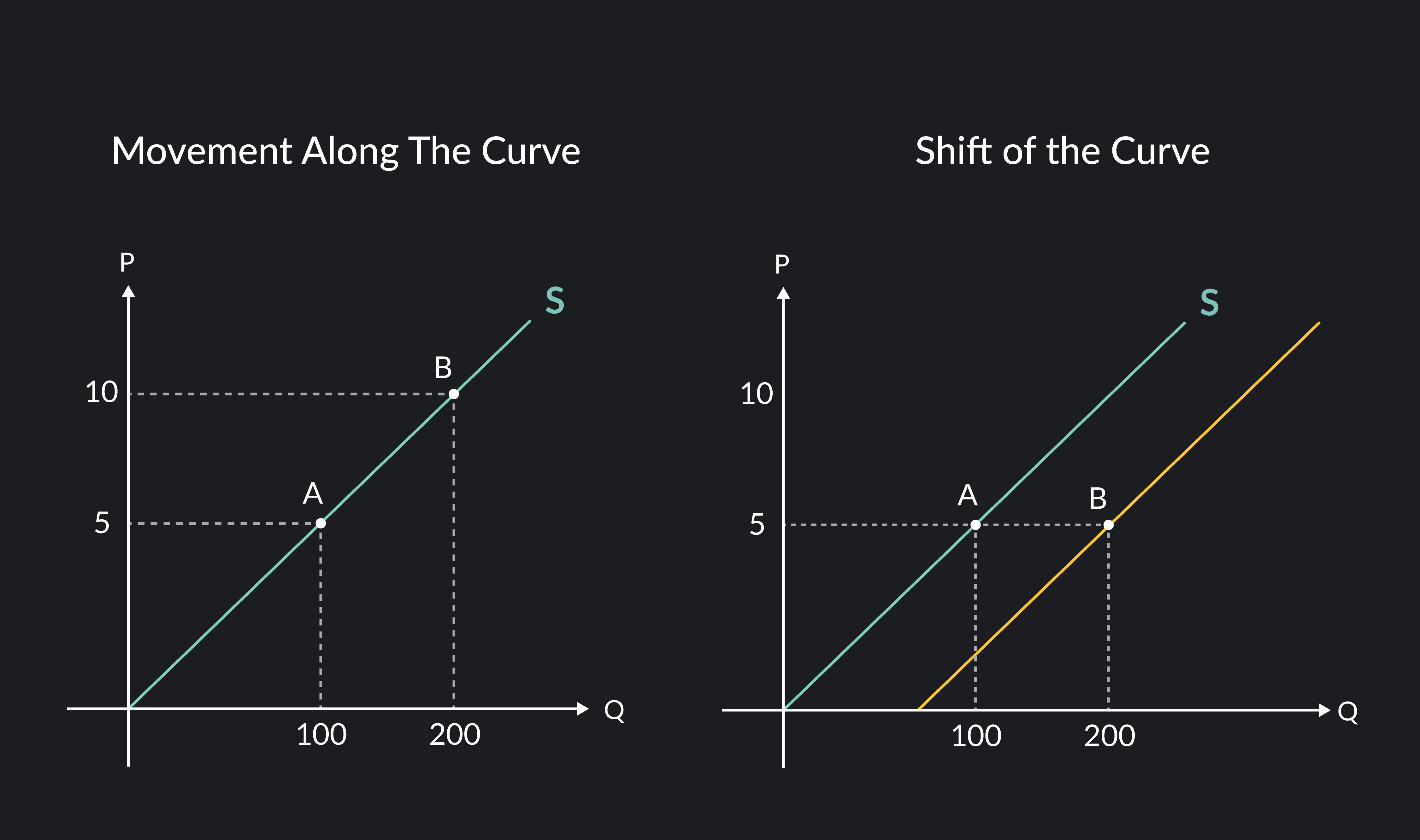
Understanding the Supply Curve & How It Works Outlier

DIY ECON How to Draw a Supply Curve and Learn the Law of Supply YouTube
How To Draw Supply And Demand Curve Flatdisk24
In The Graph, We See Two Axes.
If The Available Quantity Of The Good Increases, The Supply Curve Shifts Right.
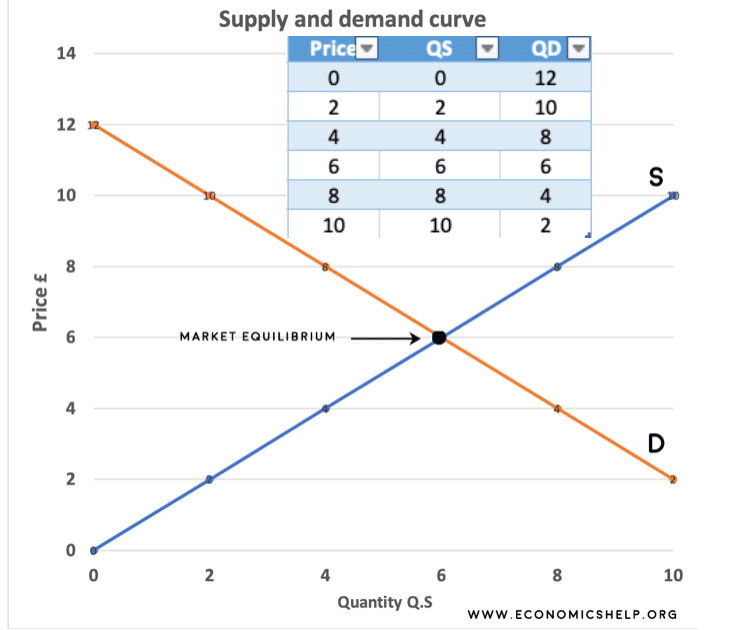
Web Plotting Price And Quantity Supply.
4.4K Views 7 Years Ago Economics.
Related Post: