How To Draw Marginal Cost Curve
How To Draw Marginal Cost Curve - To find this, we need to simply take the derivative of the total cost function: 1.6m views 9 years ago micro unit 3: Web when we add external costs to private costs, we create a marginal social cost curve. Web watch this video to learn how to draw the various cost curves, including total, fixed and variable costs, marginal cost, average total, average variable, and average fixed costs. M c(q) = dc(q) dq m c ( q) = d c ( q) d q. At this quantity, we make 2 cents profit per gallon, totaling $180 profit. The cost of producing a firm’s output depends on how much labor and capital the firm uses. Marginal cost is often graphed together with the average curves (as shown in figure 11.14). Web unfortunately the expression cannot be simplified further satisfactorily, but thankfully, this suffices for our purpose, as we can alternatively prove by showing that the same expression repeats at the minimum point of ac. Web understand the terms associated with costs in the short run—total variable cost, total fixed cost, total cost, average variable cost, average fixed cost, average total cost, and marginal cost—and explain and illustrate how they are related to each other. Learn about rational production quantity using an orange juice example. M c(q) = dc(q) dq m c ( q) = d c ( q) d q. In the presence of a negative externality (with a constant marginal external cost), this curve lies above the supply curve at all quantities. Find δc/δq by dividing the value obtained in step 1 by. We calculate marginal cost (mc) by taking the change in total cost between two levels of output and dividing by the change in output. The marginal cost is the rate of change of the total cost as output increases, or the slope of the total cost function, c(q) c ( q). Those, in turn, consist of the portions of marginal. Web unfortunately the expression cannot be simplified further satisfactorily, but thankfully, this suffices for our purpose, as we can alternatively prove by showing that the same expression repeats at the minimum point of ac. Web explore the relationship between marginal cost, average variable cost, average total cost, and average fixed cost curves in economics. Because the short run marginal cost. The purpose of analyzing marginal cost is to determine at what point an organization can. The marginal cost is the rate of change of the total cost as output increases, or the slope of the total cost function, c(q) c ( q). Find δc/δq by dividing the value obtained in step 1 by the value obtained in step 2. Web in this video we calculate the costs of producing a good, including fixed costs, variable costs, marginal cost, average variable cost, average fixed cost, and average total cost. Analyze the relationship between marginal and average costs. In this video i explain how to draw and analyze the cost curves. We do this by differentiating ac: 1.6m views 9 years ago micro unit 3: Web another cost concept that we get from the total cost function is marginal cost (mc). We calculate marginal cost (mc) by taking the change in total cost between two levels of output and dividing by the change in output. 19k views 7 years ago microeconomics (entire playlist) this video shows how to graph the marginal cost curve using the production possibilities frontier and/or. See how to graph these curves and highlights their intersections, which represent minimum points for average costs. Web understand the terms associated with costs in the short run—total variable cost, total fixed cost, total cost, average variable cost, average fixed cost, average total cost, and marginal cost—and explain and illustrate how they are related to each other. Web explore the relationship between marginal cost, average variable cost, average total cost, and average fixed cost curves in economics. To find this, we need to simply take the derivative of the total cost function: Web three cost curves (source:
How to Find Marginal Cost 11 Steps (with Pictures) wikiHow
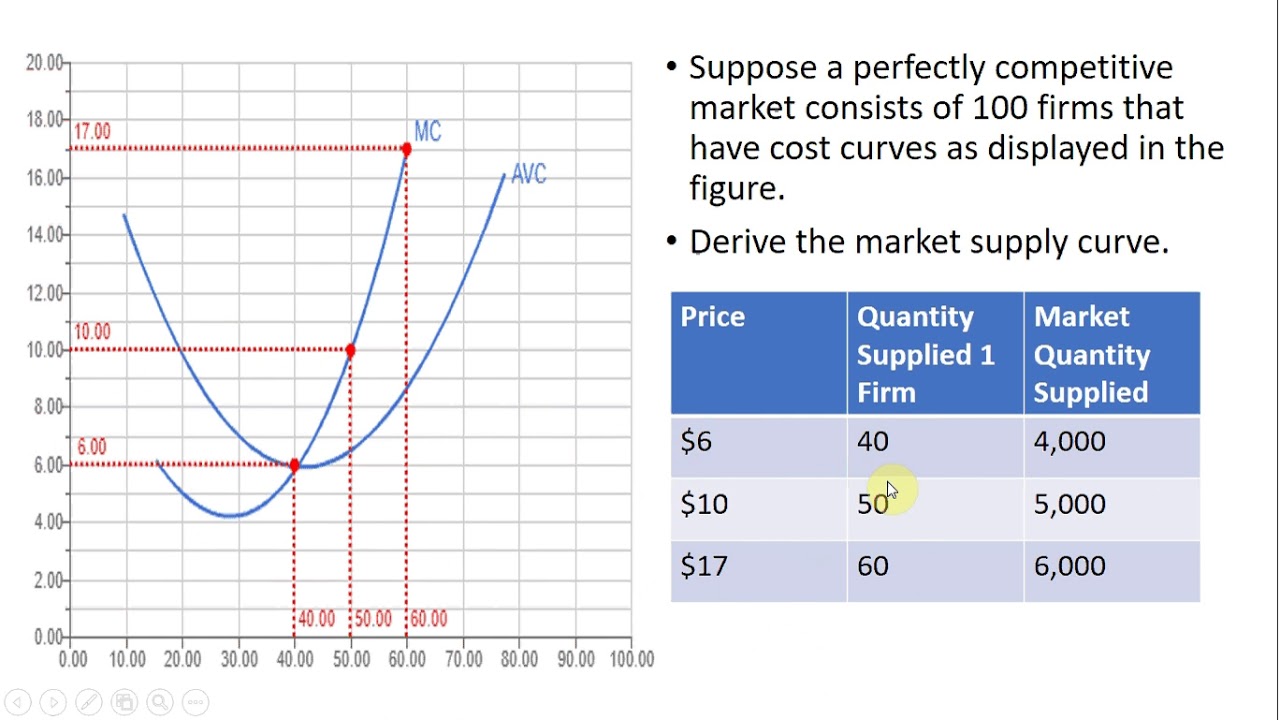
Marginal Cost Curve, Firm Supply Curve, and Market Supply Curve YouTube
Marginal Revenue Explained, With Formula and Example
In The Presence Of A Negative Externality (With A Constant Marginal External Cost), This Curve Lies Above The Supply Curve At All Quantities.
Like Average Costs, Mc Is A Rate And It Comes In $/Unit.
Journal Of Applied Mathematics) Marginal Cost Formula.
But, When Marginal Cost Is Above The Average Cost,.
Related Post: