How To Draw A Force Diagram
How To Draw A Force Diagram - Web this physics video tutorial explains how to draw free body diagrams for different situations particular those that involve constant velocity and constant acceleration. Web steps for drawing a force diagram: 9.4k views 6 years ago. What is the difference between a force diagram and a. Draw a vector to represent each force. Web a) make sure that for any free body diagram you draw, you are capable of making a complete table of forces. This video tutorial lesson discusses force as a vector and explains how force diagrams are used to describe the magnitude and direction of the individual for. How to find horizontal and vertical components of an angled force using trigonometry. How does a force diagram work? Web a free body diagram, or force diagram, is a rough sketch that shows the relative magnitude and direction of all the forces acting on a system. Dm dx = v (x) d m d x = v ( x) dv dx = −w(x) d v d x = − w ( x) d2m dx2 = −w(x) d 2 m d x 2 = − w ( x) or: Web steps for drawing a force diagram: You are not required to provide a table of forces with. Web how to draw force diagrams. Web this physics video tutorial explains how to draw free body diagrams for different situations particular those that involve constant velocity and constant acceleration. Web the force diagrams interactive video tutorial discusses force as a vector and explains how force diagrams are used to describe the magnitude and direction of the individual forces acting. Draw the object in isolation with the forces that act on it; You are not required to provide a table of forces with every free body diagram you draw, but you should expect to be called upon to create a table of forces more than once. The video lesson answers the following questions: Identify the object you will draw a. This video tutorial lesson discusses force as a vector and explains how force diagrams are used to describe the magnitude and direction of the individual for. Where there is a dot,. Identify all the forces acting directly on the object and the object exerting them. Identify the body/object you want to make an fbd of. Web table of contents show. (if there are multiple objects of interest, you will need to draw multiple diagrams.) identify all the forces acting directly on the object and the object exerting them. Identify the object you will draw a diagram for. What is the difference between a force diagram and a. There are various forces that can be acting on the object, such as applied force, frictional force, normal force, and gravitational force. Substitute terms from the force diagram for fnet. Web steps for drawing a force diagram: Dm dx = v (x) d m d x = v ( x) dv dx = −w(x) d v d x = − w ( x) d2m dx2 = −w(x) d 2 m d x 2 = − w ( x) or: 9.4k views 6 years ago. Web a free body diagram, or force diagram, is a rough sketch that shows the relative magnitude and direction of all the forces acting on a system. By the end of the section, you will be able to: So, if there is a constant distributed load, then the slope of shear will be linear and the slope of the moment will be parabolic.
Force diagrams hallmain
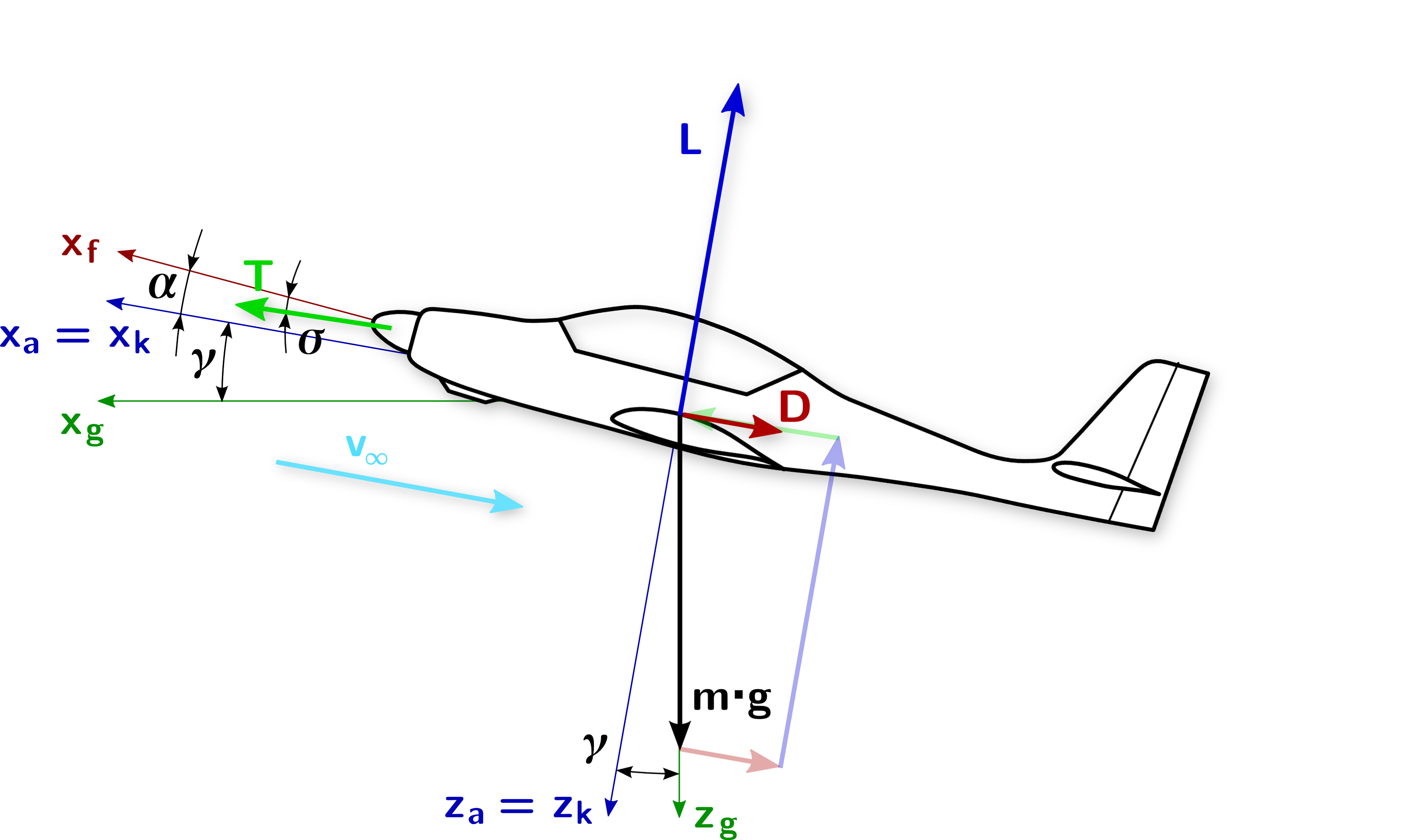
Force Diagrams 101 Diagrams

Force Diagrams 101 Diagrams
18K Views 7 Years Ago.
Δv = ∫ W(X)Dx Δ V = ∫ W ( X) D X.
Web Sal Explains How To Draw Free Body Diagrams When Forces Are Applied At An Angle.
Let's Look For What The Object Is Touching By Outlining The Object (See Figure 1 Below).
Related Post: