Glycogen Drawing
Glycogen Drawing - Magnify both linear and branching segments. It is the animal analog to starch. Web what i wanted to do in this video is familiarize ourselves with one of the most important molecules in biology and that is glucose sometimes referred to as dextrose and the term dextrose comes from the fact that the form of glucose typically. The polysaccharide structure of glucose shows the primary storage form of glucose in the body. Glycogen is the main storage form of glucose, and is key to mobilizing glucose stores in skeletal muscles. Understand the pathways by which glycogen is synthesized and broken down. Web 20k views 4 years ago biochemistry structures. Names and structures of carbohydrates. Web glycogen is a polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in fungi and animals. It comes from carbohydrates (a macronutrient) in certain foods and fluids you consume. Glycogen is a branched polysaccharide (also called a polycarbohydrate) composed of many glucose molecules linked together. Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in animals and humans which is analogous to the starch in plants. Starch and glycogen are polysaccharides. Glucose (sugar) is your body’s main source of energy. Figure 1 depicts a four unit glycogen polysaccharide. Glucose is stored in the form of glycogen in the liver (~10%) and muscles (~2%). Glycogen is homopolysachharide, made up of alpha d glucose monomers. Web session learning objective 4. Glycogen is the major storage form of glucose in the human body. Web when fasting, animals draw on these glycogen reserves during the first day without food to obtain the. It is highly concentrated in the liver, although skeletal muscles contain the most glycogen by weight. Web 20k views 4 years ago biochemistry structures. Contrast the use of glycogen in liver and muscle. Web session learning objective 4. Web this chapter discusses the historical progression of glycogen research and its current condition with particular emphasis on how it has benefitted. Web glycogen is a polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in fungi and animals. Glycogen does not exist in plant tissue. Glycogen is synthesized and stored mainly in the liver and the muscles. Three examples of homopolysaccharides, glycogen/starch, cellulose, and chitin are shown below. Glycogen tetramer (c_24 h_42 o_21) this molecule is a good representation of the structural aspects of glycogen, because it clearly depicts the. Glucose is stored in the form of glycogen in the liver (~10%) and muscles (~2%). Glycogen, a complex branched biopolymer, is primarily composed of glucose units. When energy is required by the body, glycogen in broken down to glucose, which then enters the glycolytic or pentose phosphate pathway or is released. Web when fasting, animals draw on these glycogen reserves during the first day without food to obtain the glucose needed to maintain metabolic balance. Web glycogen is the endogenous polymer. Glycogen is the major storage form of glucose in the human body. Starch and glycogen are polysaccharides. This video explains about structure of glycogen. Polysaccharides are macromolecules that are polymers formed by many monosaccharides joined by glycosidic bonds in a condensation reaction to form chains. Glycogen is a large, branched polysaccharide that is the main storage form of glucose in animals and humans. Web session learning objective 4.
Biochemistry Glossary Glycogen Structure & Synthesis Draw It to Know It

Glycogen molecule Royalty Free Vector Image VectorStock
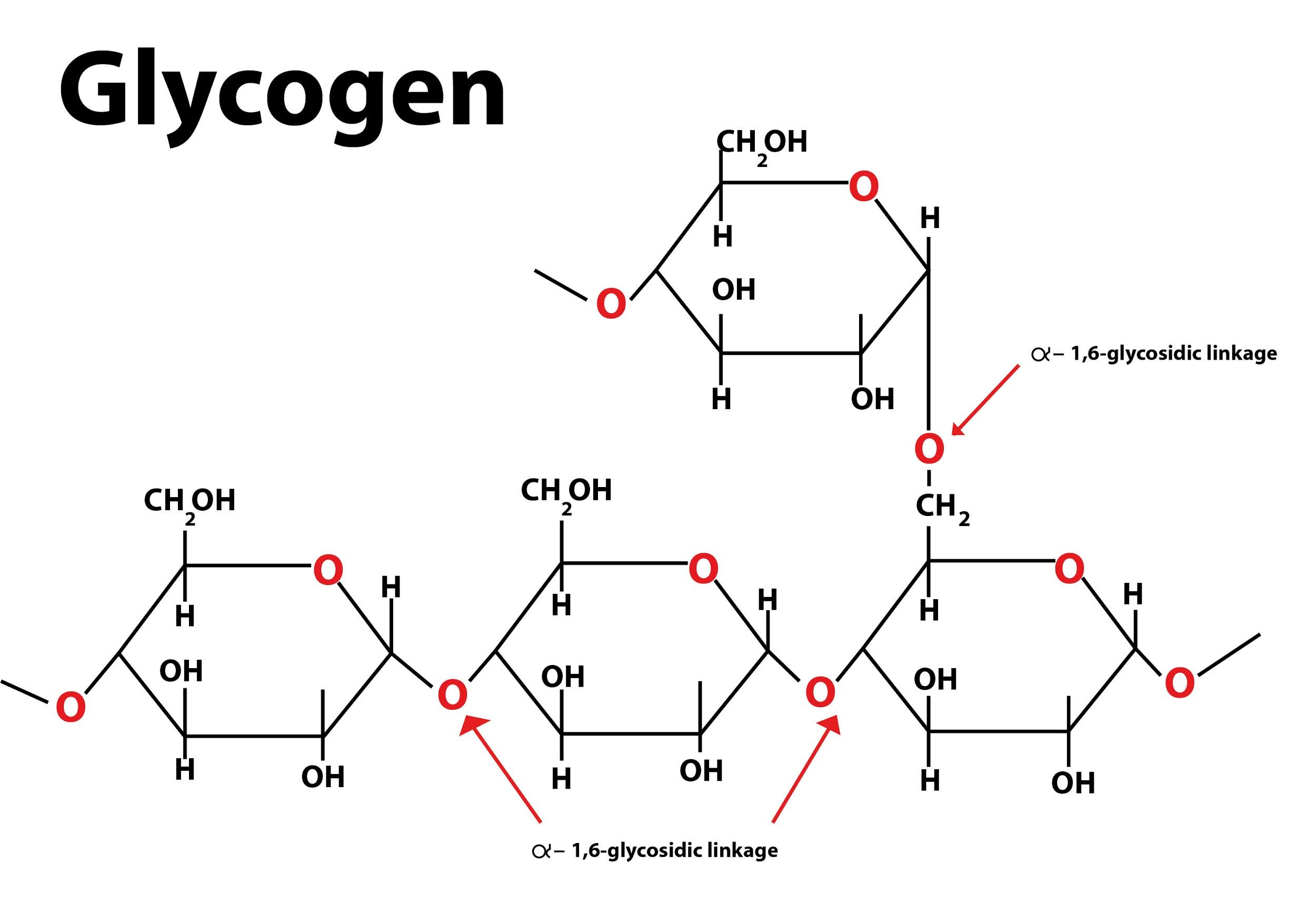
Glycogen Structure Diagram
It Is The Animal Analog To Starch.
It Comes From Carbohydrates (A Macronutrient) In Certain Foods And Fluids You Consume.
Figure 1 Depicts A Four Unit Glycogen Polysaccharide.
Web What I Wanted To Do In This Video Is Familiarize Ourselves With One Of The Most Important Molecules In Biology And That Is Glucose Sometimes Referred To As Dextrose And The Term Dextrose Comes From The Fact That The Form Of Glucose Typically.
Related Post: