Freezing Point Drawing
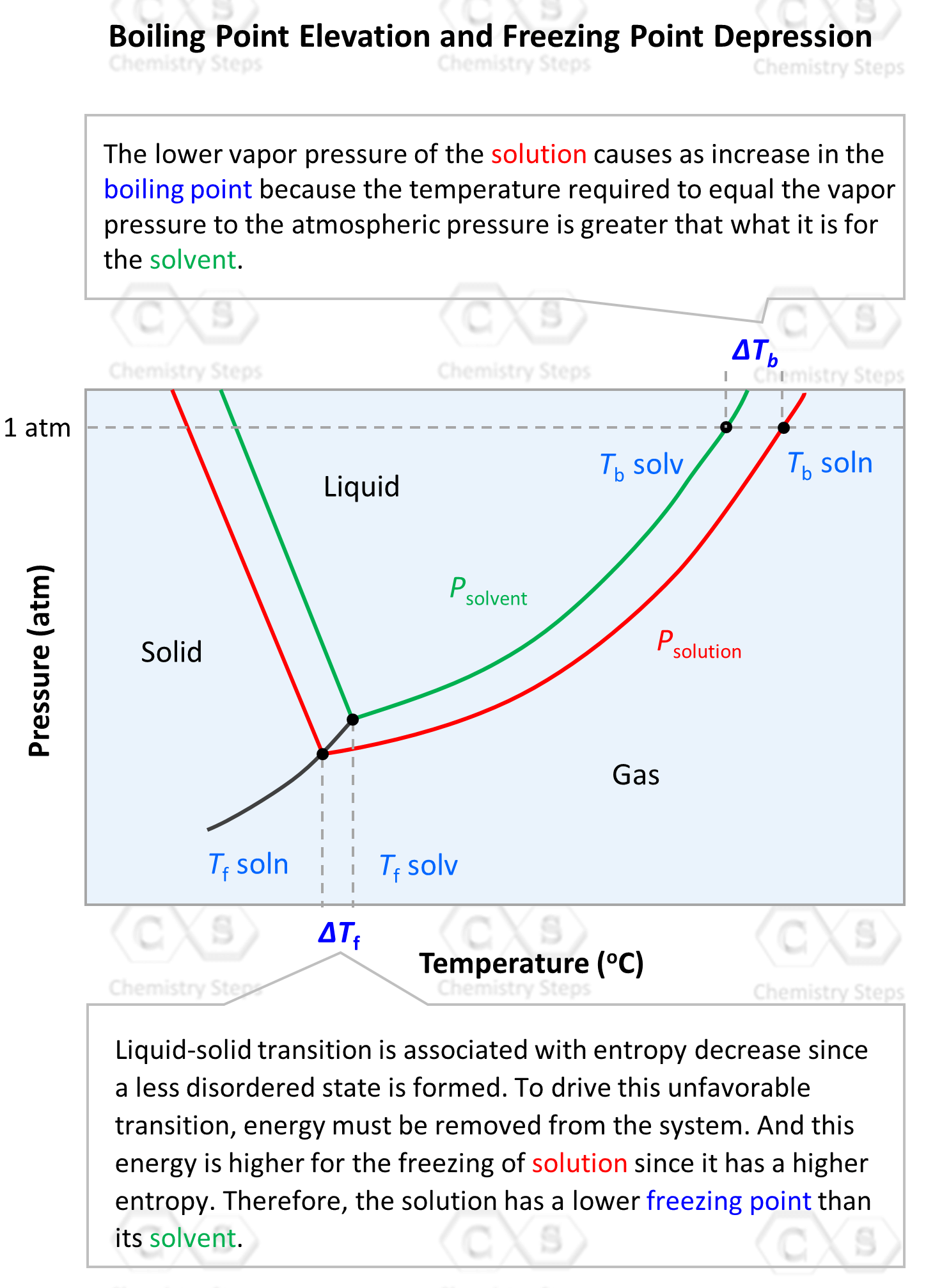
Freezing Point Drawing - Web updated on july 07, 2019. As a result, the freezing point of a solvent decreases when any solute is dissolved into it. An equation has been developed for this behavior. The freezing point of the solvent in a solution changes as the concentration of the solute in the solution changes (but it does. Web valton tyler, freezing point, 1971, etching on paper, 23 inches x 34.5 inches, tyler museum of art. Make sure you choose appropriate scales on both axis, and Web a solution will solidfy (freeze) at a lower temperature than the pure solvent. Δtf = tf(solvent) −tf(solution) = kf × m. Web the freezing point depression is the difference in temperature between the freezing point of the pure solvent and that of the solution. Web freezing point depression refers to the lowering of the freezing point of solvents upon the addition of solutes. A sample vapor pressure diagram for a pure solvent and its solution is shown below. Web freezing point depression is a colligative property observed in solutions that results from the introduction of solute molecules to a solvent. Web the freezing point of water is 32 degrees fahrenheit, 0 degrees celsius, and 273.15 kelvin. Web the addition of one mole (molecular. In this experiment, you will determine the freezing point of cyclohexane and the freezing point of a solution containing a weighed amount of unknown solute and cyclohexane. The solution has a lower freezing point than that of the pure solvent. The depression in the freezing point of a solution can be described by the following formula. Observe the challenges of. Indicate what happens to the boiling point and the freezing point of a solvent when a solute is added to it. Web on the graph, the freezing point depression is represented by δ t f. Make sure you choose appropriate scales on both axis, and Web a solution will solidfy (freeze) at a lower temperature than the pure solvent. You. The freezing points of solutions are all lower than that of the pure solvent and is directly proportional to the molality of the solute. Make sure you choose appropriate scales on both axis, and The freezing point constant, \(k_f\), for water is \(1.86^\text{o} \text{c/m}\). Web k b is the molal freezing point depression constant, and mis the molal concentration of the solute in the solution. This is the colligative property called freezing point depression. Web a solution will solidfy (freeze) at a lower temperature than the pure solvent. Examples of freezing point depression. The vapor pressure of a solution (blue) is lower than the vapor pressure of a pure solvent (pink). Web valton tyler, freezing point, 1971, etching on paper, 23 inches x 34.5 inches, tyler museum of art. Normal freezing point, o c: The solution has a lower freezing point than that of the pure solvent. It is a colligative property of solutions that is generally proportional to the molality of the added solute. Web the van't hoff factor. For example, the freezing point of seawater is lower than that of pure water. This means that a solution must be cooled to a lower temperature than the pure solvent in order for freezing to occur. Temperature given as °c, °f, k and °r.
Melting Point, Boiling Point and Freezing Point Chemistry YouTube
Freezing Point Depression Chemistry Steps

Boiling and Evaporation, Freezing and Melting Points of Water Stock
You Will Determine The Molar Mass Of The Unknown Solute Based On The Decrease In The Freezing Point.
Explain What The Term Colligative Means, And List The Colligative Properties.
Note That The Molal Freezing Point Depression Constant, K F, Has A Specific Value Depending On The Identity Of The Solvent.
Web The Freezing Point Of Water Is 32 Degrees Fahrenheit, 0 Degrees Celsius, And 273.15 Kelvin.
Related Post: