Drawing Of The Rock Cycle
Drawing Of The Rock Cycle - The rock cycle includes igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks. Existing rock or organic material needs to be weathered, eroded (removed), transported, and finally deposited. Igneous rocks form when magma or lava cools and solidifies. Web find out more about the different rock types in this guide. The sediment can then be transported by wind, water, or ice and deposited in layers. Each of these rocks are formed by physical changes—such as melting, cooling, eroding, compacting, or deforming —that are part of the rock cycle. Web the rock cycle diagram. Magma that reaches earth’s surface through volcanic activity is called lava. Students draw and picture the 'recycling' of rock through illustrations or flowcharts. Igneous rocks form from the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. Web engage with a free rock cycle diagram activity on storyboard that. This is known because of the break along a flat parallel surface, visual mineral grains, mineral grains cemented together, soft and crumbly, light right and has no holes. Components of the rock cycle. (1) earth’s internal heat engine, which moves material around in the core and the mantle. Igneous rocks form when magma or lava cools and solidifies. Look at the diagram to get a better understanding of all the different processes of the rock cycle. It is a continuous process that is driven by various geological forces, including heat, pressure, weathering, and erosion. (1) earth’s internal heat engine, which moves material around in the core and the. It is occurring continuously in nature through geologic time. Existing rock or organic material needs to be weathered, eroded (removed), transported, and finally deposited. Web the rock cycle diagram. When rocks are pushed deep below earth’s surface, they can melt to form magma. For example, sedimentary rock shale becomes slate when heat and pressure are added. Web moomoomath and science. 1 the rock cycle explained. Igneous rocks form from the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. 55k views 3 years ago. Igneous rocks form when magma or lava cools and solidifies. The rock cycle includes igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks. This is known because of the break along a flat parallel surface, visual mineral grains, mineral grains cemented together, soft and crumbly, light right and has no holes. A useful way to illustrate how the three main types of rock are related to one another and how changes to rocks happen in a recurring sequence is the rock cycle. Web the rock cycle begins with the formation of igneous rocks through volcanic activity or the cooling of magma beneath the earth’s surface. Web the rock cycle is a series of processes that transform one rock type into another. The rock cycle and plate tectonics [1] Web what is a rock cycle diagram? These processes create three main types of rocks: Web the rock cycle is driven by two forces: Web the rock cycle diagram. Web find out more about the different rock types in this guide.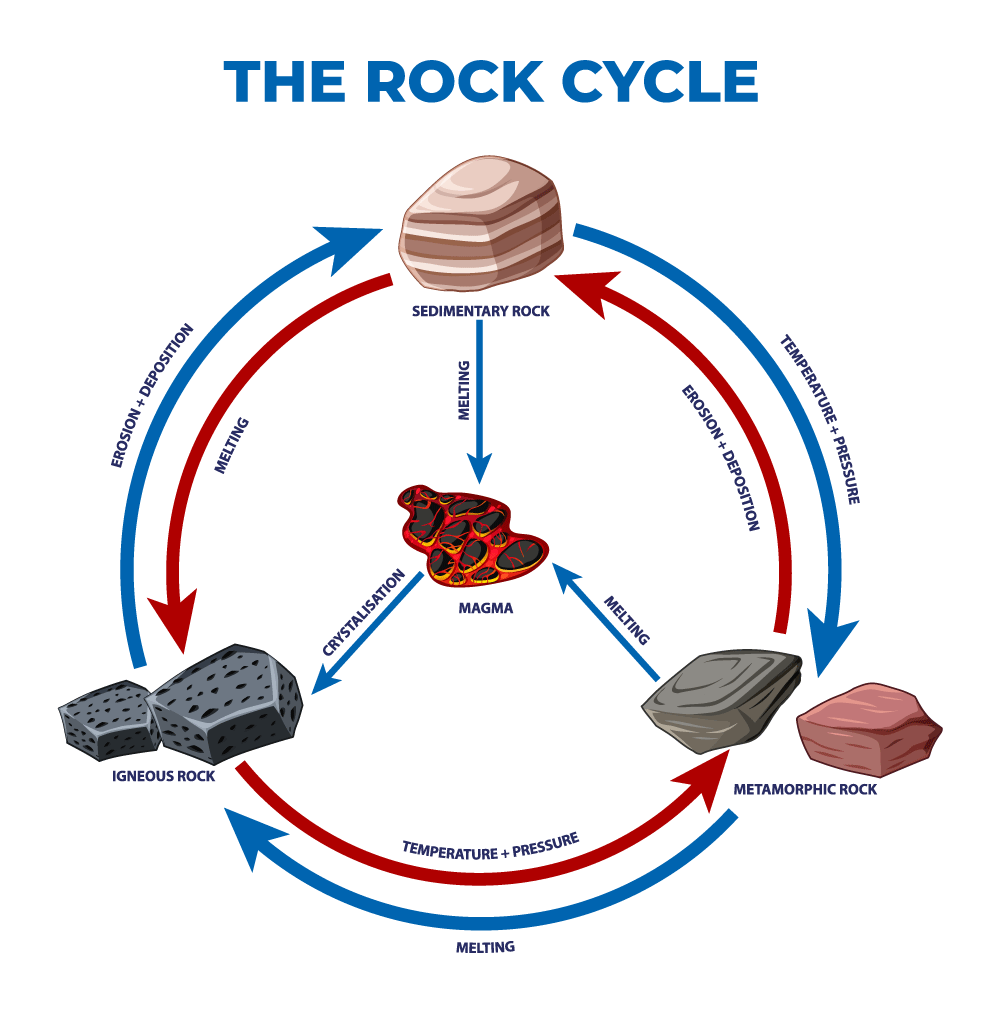
Rock Cycle Transition, Factors, and Evolving Process

The Rock Cycle Learn The Types Of Rocks & Minerals
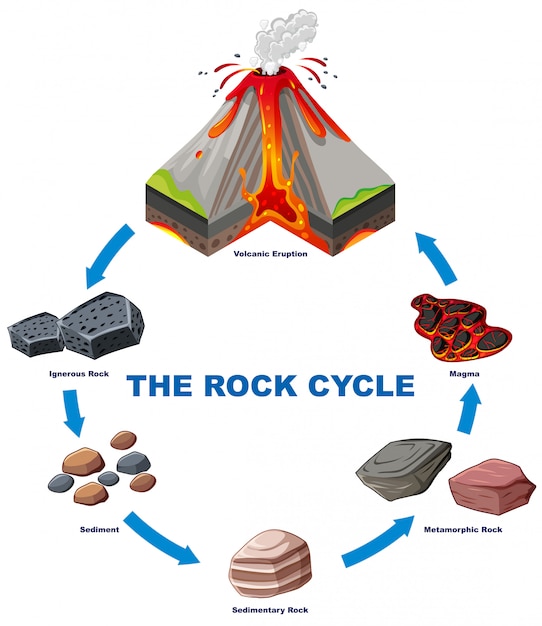
Free Vector Diagram showing rock cycle
Web Rocks Are Broadly Classified Into Three Groups:
(1) Earth’s Internal Heat Engine, Which Moves Material Around In The Core And The Mantle And Leads To Slow But Significant Changes Within The Crust, And (2) The Sun Which Powers The Hydrological Cycle, Moving Water, Wind And Air Along Earth’s Surface.
When Rocks Are Pushed Deep Below Earth’s Surface, They Can Melt To Form Magma.
It Is A Continuous Process That Is Driven By Various Geological Forces, Including Heat, Pressure, Weathering, And Erosion.
Related Post: