Drawing Dna Replication
Drawing Dna Replication - Web this is illustrated in the below diagram, using correct pairings of nucleotides. Similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic dna replication. Explain why okazaki fragments are formed. Web the puzzlement surrounding how replication proceeds begins with experiments that visualize replicating dna. When a cell divides, it is important that each daughter cell receives an identical copy of the dna. The leading strand is built continuously, while the lagging strand is built in fragments, called okazaki fragments. Each strand then serves as a template for a new dna molecule. The scope of the problem. Describe the process of dna replication and the functions of the enzymes involved. Web the process of dna duplication is called dna replication. The scope of the problem. Replication fork formation and its function. As you will soon see, the model predicts how the dna sequence can code for proteins, and how the molecule can be replicated. Dna is the information molecule. There were three models suggested for dna replication: Web the process of dna duplication is called dna replication. In this section, we explore how an elaborate “replication machine” achieves this accuracy, while duplicating dna at rates as high as 1000 nucleotides per second. Web dna replication occurs through the help of several enzymes. Replication fork formation and its function. Web in molecular biology, [1] [2] [3] dna replication. Similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic dna replication. When a cell divides, it is important that each daughter cell receives an identical copy of the dna. Web dna replication occurs through the help of several enzymes. There were three models for how organisms might replicate their dna: New dna is made by enzymes called dna polymerases, which require a template and. The point at which the replication begins is known as the origin of replication (oric). This continuous sequence, and the sequence they are in determine an organisms’ structural, physical and anatomical features. It is the region where the dna is unzipped. Web initiation, elongation and termination are three main steps in dna replication. These enzymes unzip dna molecules by breaking the hydrogen bonds that hold the two strands together. The semiconservative model of dna replication is shown. How do these four structures form dna? Dna replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part of biological inheritance. The conservative method of replication suggests that parental dna remains together and. In this section, we explore how an elaborate “replication machine” achieves this accuracy, while duplicating dna at rates as high as 1000 nucleotides per second. Web following are the important steps involved in dna replication: All organisms must duplicate their dna with extraordinary accuracy before each cell division. Thus, replication cannot initiate randomly at any point in dna. New dna is made by enzymes called dna polymerases, which require a template and a primer (starter) and synthesize dna in the 5' to 3' direction. In an extremely elegant model, that's how. For the replication to begin there is a particular region called the origin of replication.![[DIAGRAM] Dna Replication Diagram Labeled](http://clipartmag.com/image/dna-drawing-labeled-36.jpg)
[DIAGRAM] Dna Replication Diagram Labeled
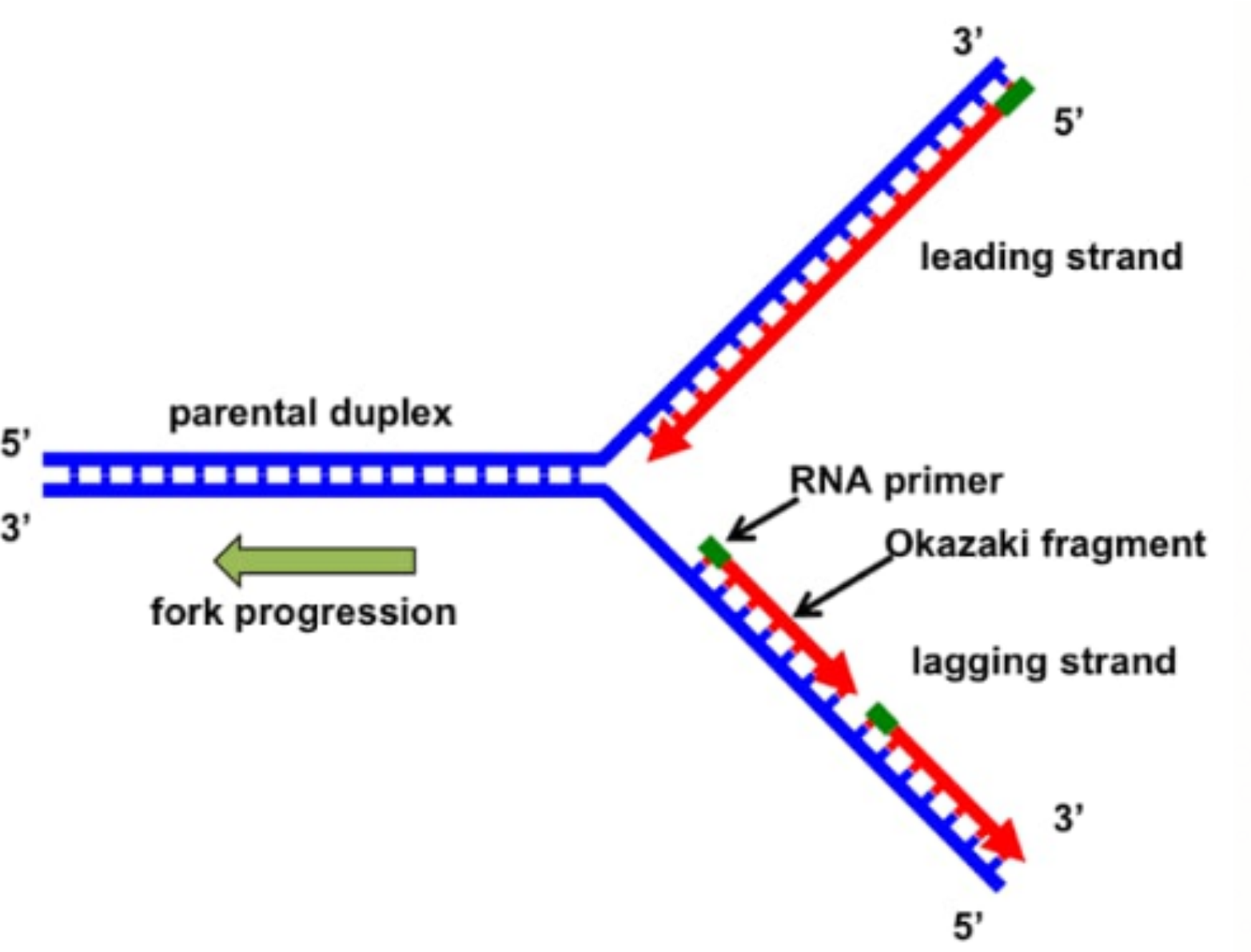
Draw a labelled schematic sketch of replication fork of DNA. Explain
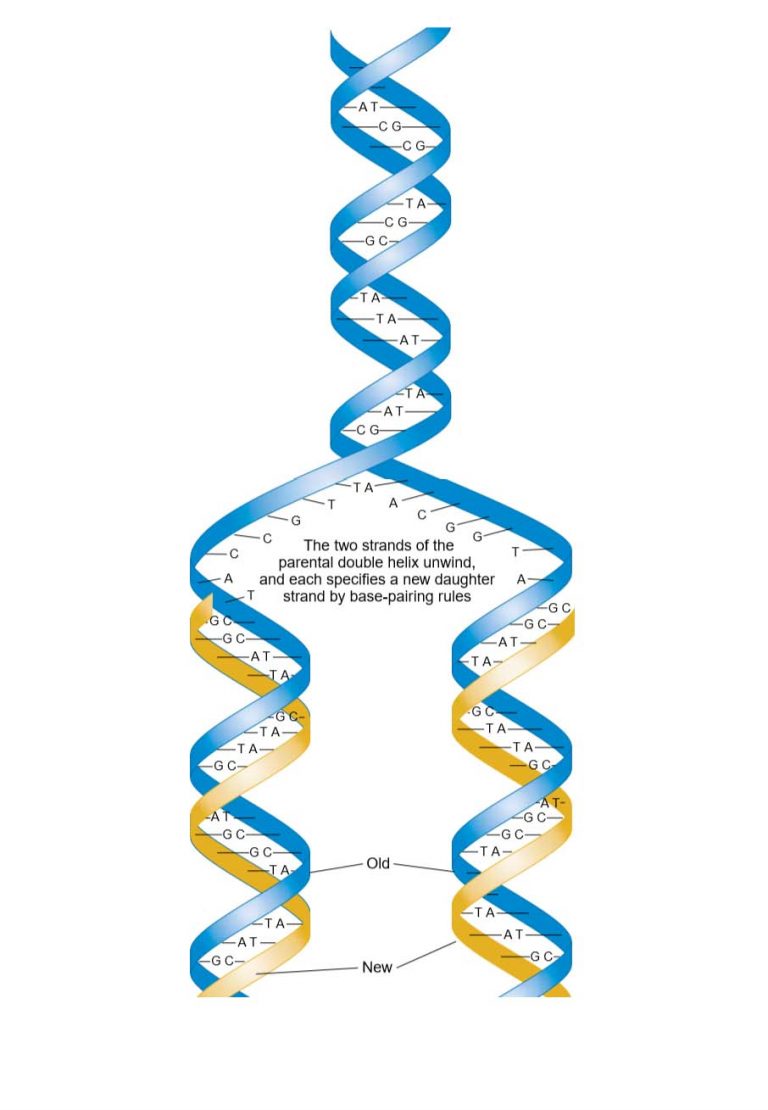
DNA Replication Study Solutions
Web This Animation From Life Sciences Outreach At Harvard University Shows A Simplified Version Of The Process Of Dna Replication.view This Video (And More Like.
Discuss The Potential Implications Of Mutations At Cellular, Organismal, And Evolutionary Levels.
It Stores Instructions For Making Other Large Molecules, Called Proteins.
Each Strand In The Double Helix Acts As A Template For Synthesis Of A New, Complementary Strand.
Related Post: