Draw Sister Chromatids
Draw Sister Chromatids - Web sister chromatids definition. Web two sister chromatids attach at a region called the centromere. Web as the two daughter dna strands are produced from the chromosomal dna during s phase, these daughter strands recruit additional histones and other proteins to form the structures known as sister. Web updated on january 23, 2019. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like draw a picture of a replicated chromosome. Crossing over occurs only during prophase i. The two identical dna molecules are identified as sister chromatids, and are held together by a single centromere. The two “sister” chromatids are joined at a constricted region of the chromosome called the centromere. These copies remain attached until sister chromatids are separated or detached during cell division. Sister chromatids are genetically identical copies or replicas of a single chromosome. Although a cell needs to undergo interphase before entering meiosis, interphase is technically not part of meiosis. During cell division, spindle fibers attach to the centromere and pull each of the sister chromatids to. • dna is replicated before meiosis so that all chromosomes consist of two sister chromatids. Crossing over occurs only during prophase i. Mitosis occurs in four. Web label the appropriate structures with these terms: Interphase is not part of meiosis. Chromosome (label as duplicated or unduplicated), centromere, kinetochore, sister chromatids, nonsister chromatids, homologous pair (use a bracket when labeling), homolog (label each one), chiasma, sister chromatid cohesion, and gene loci, labeling the alleles of the f and h genes. In metaphase i, chromosomes line up in. Web the second round of cell division is meiosis ii, in which the goal is to separate sister chromatids. Web the sister chromatids separate from one another and are pulled towards opposite poles of the cell. How do they differ?, what does diploid mean? Web eukaryotic chromosomes consist of two sister chromatids. During prophase i, chromosomes pair up and exchange. During cell division, they are separated from each other, and each daughter cell receives one copy of the chromosome. Right now, both of these two sister chromatids combined are considered to be one chromosome. These copies remain attached until sister chromatids are separated or detached during cell division. The mitotic spindle also begins to develop. Web the second meiotic division, where sister chromatids separate, is like mitosis. During prophase i, chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material, creating more variation. Sister chromatids and homologous chromosomes during interphase of the cell cycle, the dna is replicated. The mechanics of meiosis ii are similar to mitosis, except that each dividing cell has only one set of homologous chromosomes, each. Web a full set of sister chromatids is created during the synthesis ( s) phase of interphase, when all the chromosomes in a cell are replicated. This is important for chromosomal separation during cell division. The sister chromatids are identical to one another and are attached at a compressed region called the centromere. • dna is replicated before meiosis so that all chromosomes consist of two sister chromatids. During cell division, spindle fibers attach to the centromere and pull each of the sister chromatids to. Web two sister chromatids attach at a region called the centromere. How do they differ?, what does diploid mean? Web during dna duplication in the s phase, each chromosome is replicated to produce two identical copies, called sister chromatids, that are held together at the centromere by cohesin proteins.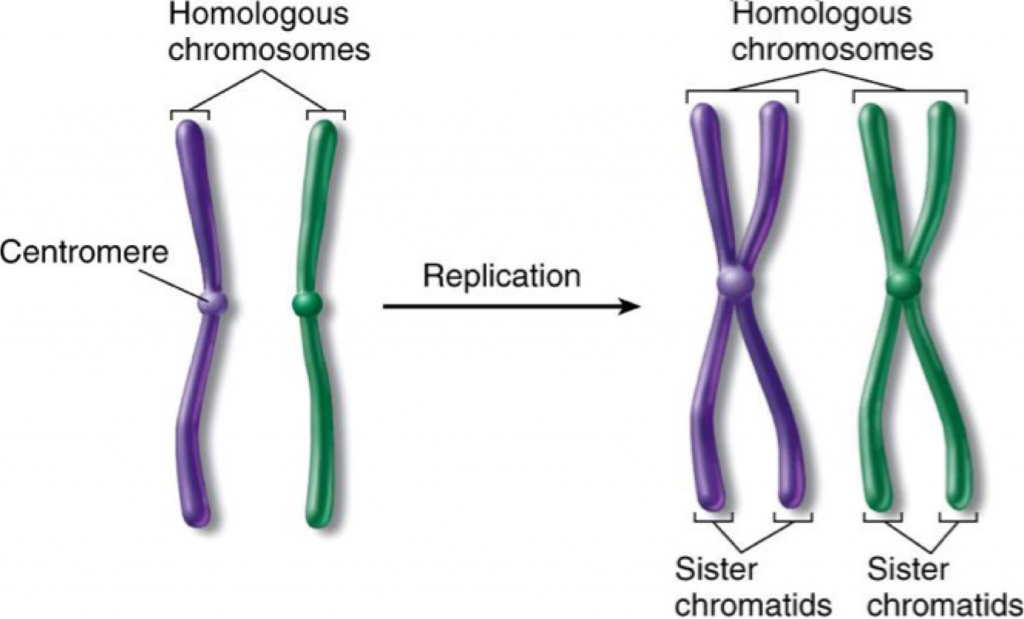
3.2 Chromosomes The Biology Classroom
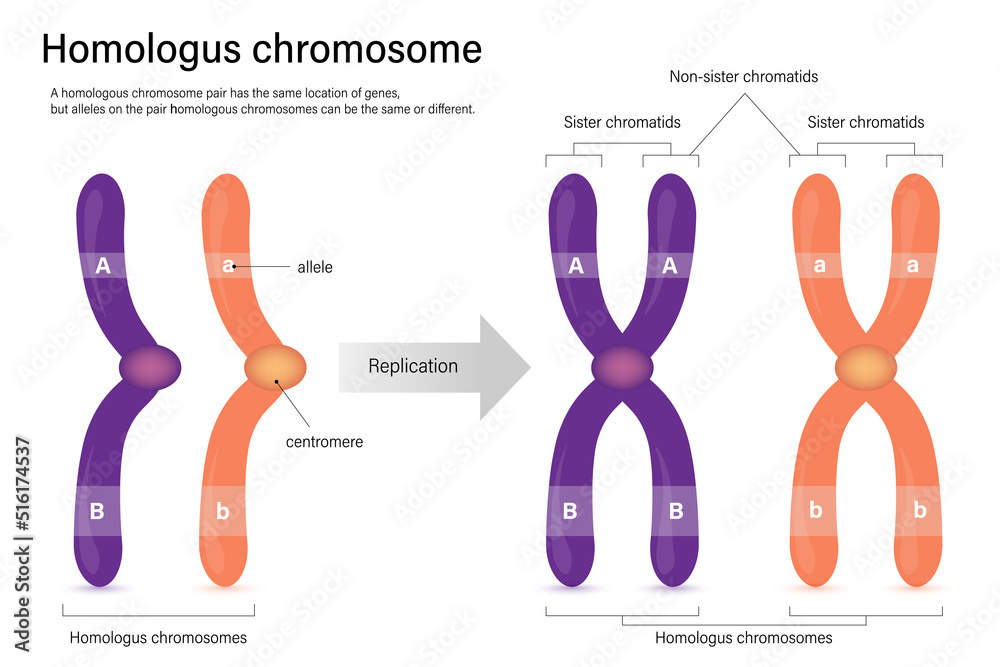
Diagram of homologus chromosome. Sister chromatids and Nonsister

13.1 DNA Biology LibreTexts
Web Label The Appropriate Structures With These Terms:
Mitosis Occurs In Four Phases.
Web Study With Quizlet And Memorize Flashcards Containing Terms Like Draw A Picture Of A Replicated Chromosome.
Interphase Is Not Part Of Meiosis.
Related Post: