Draw Glycolysis
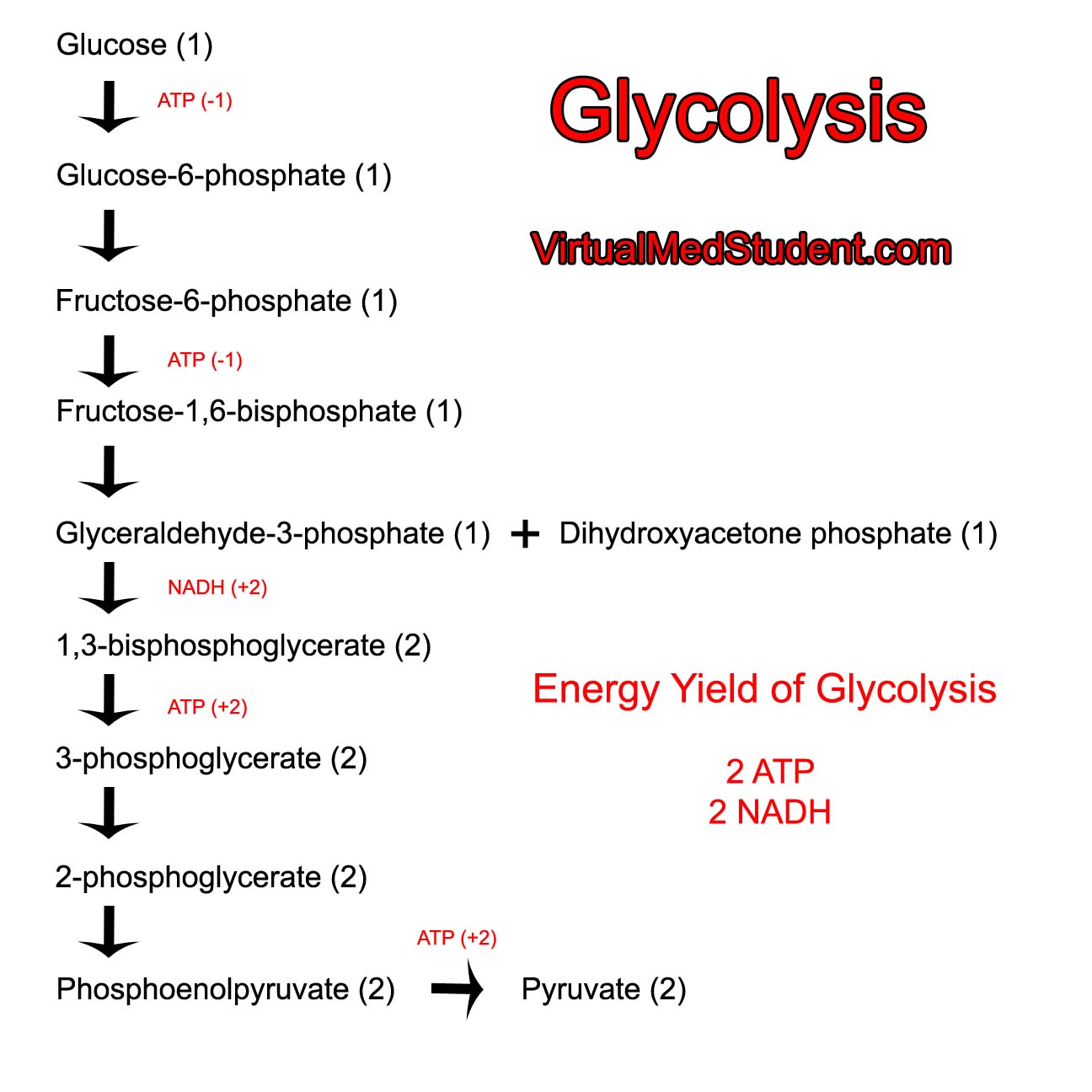
Draw Glycolysis - This will be discussed in more detail below. Web glycolysis involves 10 reactions that take place in the cytosol and generates two atp molecules without the requirement of molecular oxygen. Glycolysis is an ancient metabolic pathway, meaning that it evolved long ago, and it is found in the great majority of organisms alive today 2, 3 . Afterwards, pyruvate can be completely oxidized to co 2 and h 2. Oxidation of glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate to 1,3, bisphospho glycerate. 1.4k views 4 years ago. It enters cells through specific transporter. In fact, nearly all living organisms carry out glycolysis as part of their metabolism. Follow along with the video to draw out the steps of glycolysis and fermentation. Glycolysis is an almost universal central pathway of glucose catabolism. In glycolysis, glucose is converted into pyruvate. Web glycolysis is the metabolism of glucose into two pyruvate molecules, with the net generation of two molecules of atp and two molecules of nadh. Web glycolysis is the process in which glucose is broken down to produce energy. You may draw the structures in any arrangement that you like, so long as. This will be discussed in more detail below. Interconversion of the triose phosphates. Web let's explore the process of glycolysis, the first phase of cellular respiration. Role of glycolysis in producing atps and nadhs and converting glucose to pyruvates. Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Or lactate under anaerobic conditions along with the production of a small amount of energy. Number of reactions/steps that are highly regulated during glycolysis is/are __ ☐ 3 ☐ 10 1 4. Glycolysis takes place in both aerobic and anaerobic organisms and is the first step toward the metabolism of glucose. Web glycolysis is the first step in the breakdown. In fact, nearly all living organisms carry out glycolysis as part of their metabolism. The video focuses on one of the most important metabolic pathway, glycolysis. Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Oxidation of glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate to 1,3, bisphospho glycerate. Number of reactions/steps that are highly regulated during glycolysis is/are __ ☐ 3 ☐ 10 1 4. Interconversion of the triose phosphates. Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Like the link reaction, the krebs cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. Web one of the primary mechanisms that control the regulation of the hexokinase step in glycolysis is the presence of different hexokinase enzymes in different cellular types. Web glycolysis is the metabolic process that serves as the foundation for both aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration. Web glycolysis is the major pathway for glucose metabolism in which glucose will convert to pyruvate (under aerobic condition) or lactate (anaerobic). Web draw the skeletal structure of the products formed when the given triacylglycerol is hydrolyzed with water in the presence of sodium hydroxide. In glycolysis, glucose is converted into pyruvate. During glycolysis some of the free energy is released and conserved in the form of atp and nadh. In contrast, oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria generates 30 atp molecules but requires oxygen (see chandel 2020a). It produces two molecules of pyruvate, atp, nadh and water.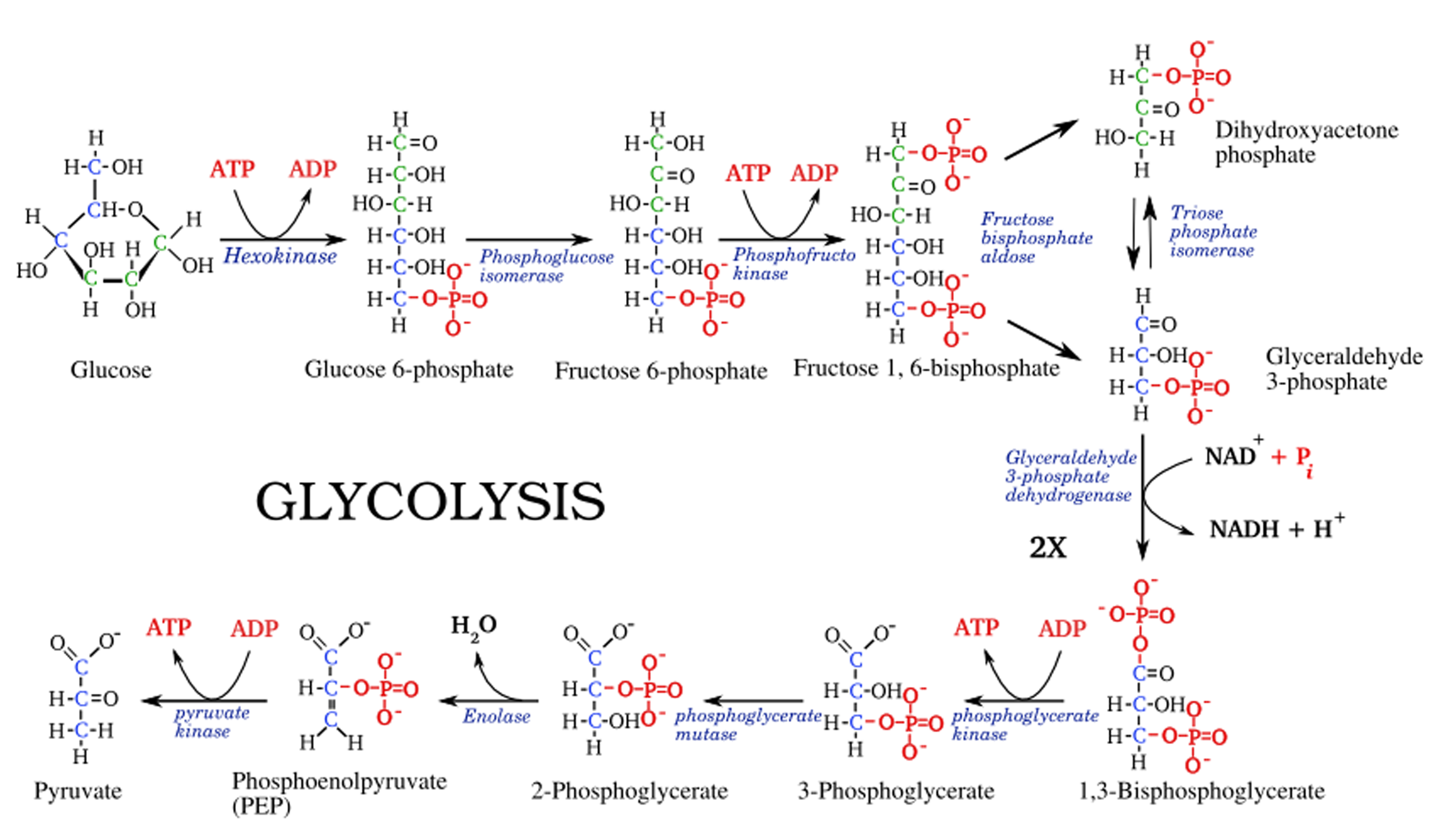
Glycolysis steps, diagram and enzymes involved Online Biology Notes
Sugar Strip Down Glycolysis and Energy Formation

What is Glycolysis? Superprof
It Is Regulated At The Entry To The Pathway And At The Irreversible Steps (1, 3, And 10).
Web Glycolysis Is The First Step In The Breakdown Of Glucose To Extract Energy For Cellular Metabolism.
Afterwards, Pyruvate Can Be Completely Oxidized To Co 2 And H 2.
Conversion Of Glucose 6 Phosphate To Fructose 6 Phosphate.
Related Post: