Draw A Mechanism For This Reaction
Draw A Mechanism For This Reaction - The arrow notation in mechanisms. A reaction mechanism is the sequence of elementary steps by which a chemical reaction occurs. Reaction arrows are found on the arrows tab. Location where a new bond should be. A reaction that occurs in two or more elementary steps is. Be sure to answer all parts. Whereas a simple equation tells you what you start with. 2 no 2 → no 3 + no (slow) no 3 + co → no 2 + co 2 (fast) each step is called an elementary step,. The decomposition of ozone, for example,. A chemical reaction often occurs in steps, although it may not always. Whereas a simple equation tells you what you start with. It describes how individual atoms, ions, or molecules interact to form particular products. It involves representing the breaking and. A chemical reaction often occurs in steps, although it may not always. Be sure to answer all parts. Web a mechanism refers to the series of steps that the reagents undergo during a chemical reaction. A reaction that occurs in two or more elementary steps is. A chemical reaction often occurs in steps, although it may not always. The decomposition of ozone, for example,. Draw a mechanism for the following reaction in the presence of a hydroxide (−oh). The decomposition of ozone, for example,. A chemical reaction often occurs in steps, although it may not always. Web this molecular description is the mechanism of the reaction; It involves representing the breaking and. Web the chemdoodle web components library is a pure javascript chemical graphics and cheminformatics library derived from the chemdoodle application and produced by. A chemical reaction often occurs in steps, although it may not always. Draw a stepwise mechanism for the following reaction: Whereas a simple equation tells you what you start with. Be sure to answer all parts. Reaction arrows are found on the arrows tab. For our first example of chemical reactivity, let’s look at a very simple reaction that occurs between hydroxide ion. The arrow notation in mechanisms. Location where a new bond should be. Web a possible mechanism for the overall reaction that explains the rate law is: A reaction that occurs in two or more elementary steps is. Web the chemdoodle web components library is a pure javascript chemical graphics and cheminformatics library derived from the chemdoodle application and produced by. Want to join the conversation? The decomposition of ozone, for example,. Web this molecular description is the mechanism of the reaction; The decomposition of ozone, for example,. Draw a mechanism for the following reaction in the presence of a hydroxide (−oh) base: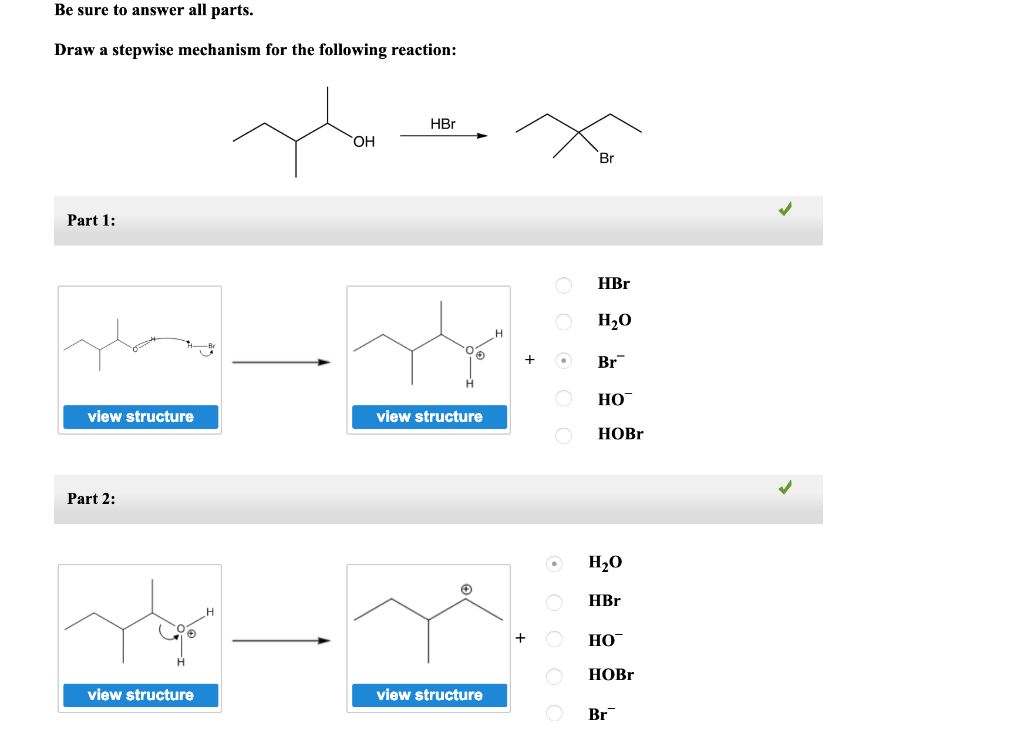
draw a stepwise mechanism for the following reaction 2xsafari
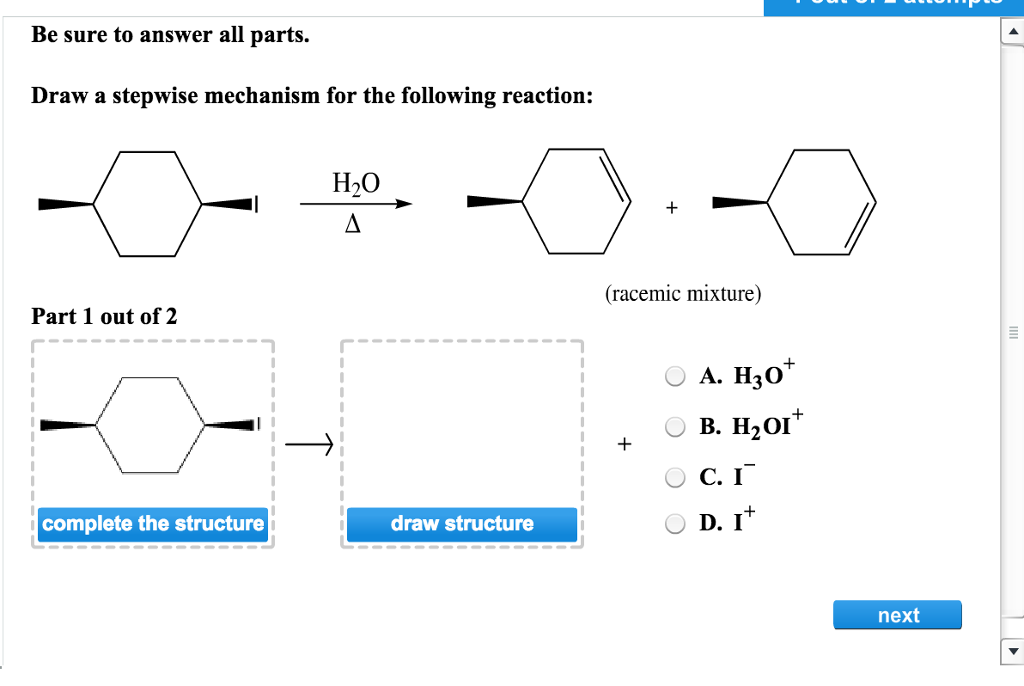
Solved Draw A Stepwise Mechanism For The Following Reacti...
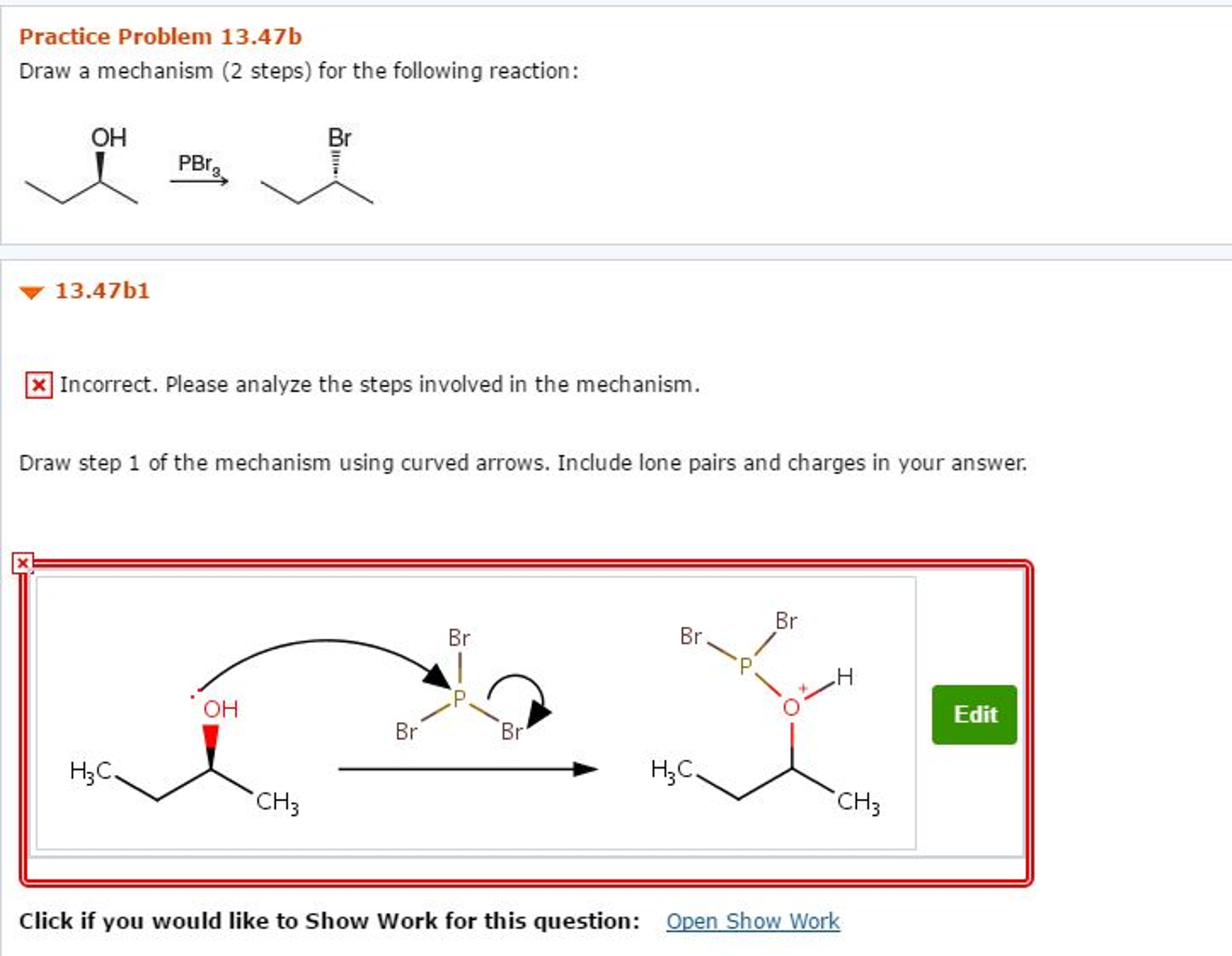
Solved Draw a mechanism (2 steps) for the following
Web The Reaction Mechanism (Or Reaction Path) Is The Process, Or Pathway, By Which A Reaction Occurs.
Since Chemical Reactions Involve The.
It Involves Representing The Breaking And.
In The Very Start How Did You Know.
Related Post: