Connective Tissue Drawing
Connective Tissue Drawing - This article will describe the cell types making up connective tissue as well as the histology and function of dense regular and dense irregular connective. Web dense regular connective tissue comprises structures such as ligaments, tendons and aponeuroses, whilst dense irregular tissue is more widely distributed throughout the body. Connective tissue is the most abundant and widely distributed of the primary tissues. By the end of this section, you will be able to: Web table of contents. A tissue is a group of cells, in close proximity, organized to perform one or more specific functions. Be able to describe the functions of cells commonly found in connective tissue and identify them. There are four basic tissue types defined by their morphology and function: Connective tissue is the tissue that connects or separates, and supports all the other types of tissues in the body. Connective tissue is classified based on the characteristics of its cellular and extracellular components. Connective tissue is classified based on the characteristics of its cellular and extracellular components. Transient cells (or wandering cells) types of connective tissue. Web the connective tissues include several types of fibrous tissue that vary only in their density and cellularity, as well as the more specialized and recognizable variants— bone, ligaments, tendons, cartilage, and adipose (fat) tissue. Connective tissue. Connective tissue fibers and matrix are synthesized by specialized cells called fibroblasts. O compare the molecular makeup, structural organization, location, and functions of the three main fiber types of connective tissue. In bone, the matrix is rigid and described as calcified because of the deposited calcium salts. Connective tissue has three main components: As may be obvious from its name,. Describe the structure and function of skeletal muscle fibers. A tissue is a group of cells, in close proximity, organized to perform one or more specific functions. Comprises cells suspended in an extracellular matrix of protein fibers and ground substance. O compare the molecular makeup, structural organization, location, and functions of the three main fiber types of connective tissue. O. Epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. Web name of structures are written right behind the drawings. Cells, fibers, and ground substance. Web identify and distinguish between the types of connective tissue: Describe the structure and function of skeletal muscle fibers. Connective tissue can be broken down into two primary categories: Web table of contents. From the connective tissue sheath that surrounds a muscle, to the tendons that attach muscles to bones, and to. Connective tissue proper connective tissue containing a viscous matrix, fibres, and cells. Web structure and cellular components of loose connective tissue. As may be obvious from its name, one of the major functions of connective tissue. O describe the general microscopic structure and function of connective tissue. O correlate morphology of resident and wandering ct cells with their locations and functions. Web some are solid and strong, while others are fluid and flexible. It would help if the action scenes were more. Define a muscle fiber, myofibril, and sarcomere.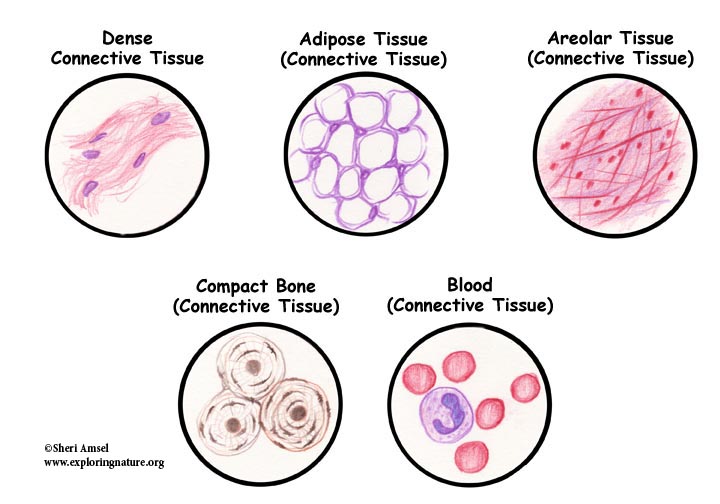
Connective Tissue

500 Connective Tissue Diagram Images, Stock Photos & Vectors Shutterstock

Mammalian Tissues Lab Notebook Students Coursework
Web Connective Tissue Type Of Tissue That Serves To Hold In Place, Connect, And Integrate The Body’s Organs And Systems.
Fig 024 Types Of Connective Tissue.
The Main Criteria Are The Type Of Cells, Arrangement And Type Of Fibers, And Composition Of The Extracellular Matrix.
Comprises Cells Suspended In An Extracellular Matrix Of Protein Fibers And Ground Substance.
Related Post: