Cell Membrane Drawing Labeled
Cell Membrane Drawing Labeled - Explain the major features and properties of the cell membrane. The cell membrane is semipermeable (or selectively permeable). Describe the molecular components that make up the cell membrane. The 3 proteins have lines with the label integral membrane proteins. An animal cell is a eukaryotic cell that lacks a cell wall, and it is enclosed by the plasma membrane. It is also simply called the cell membrane. When drawing and labeling a diagram of the plasma membrane you should be sure to include: The cell membrane or plasma membrane is a selectively permeable lipid bilayer that encloses the contents of the cell and regulates the transport of materials into and out of it. The cell membrane consists of two adjacent layers of phospholipids. Web the cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a double layer of lipids and proteins that surrounds a cell. Differentiate between materials that can and cannot diffuse through the lipid bilayer. Compare and contrast different types of passive transport with active transport, providing examples of each. The cell membrane or plasma membrane is a selectively permeable lipid bilayer that encloses the contents of the cell and regulates the transport of materials into and out of it. Explain the major. Web practice labeling the parts of the cell membrane learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free. An animal cell is a eukaryotic cell that lacks a cell wall, and it is enclosed by the plasma membrane. How easily these molecules can cross the membrane depends on their size and polarity. One of the proteins is shown with a. Its function is to protect the integrity of the interior of the cell by allowing certain substances into the cell while keeping other substances out. Differentiate between materials that can and cannot diffuse through the lipid bilayer. A cell’s plasma membrane defines the cell, outlines its borders, and determines the nature of its interaction with its environment. When drawing and. Its facts, analogy, composition, location, & functions described using examples & labeled picture. It also serves as a base of attachment for the cytoskeleton in some. Compare and contrast different types of passive transport with active transport, providing examples of each. Web the plasma membrane is the border between the interior and exterior of a cell. It separates the cytoplasm (the contents of the cell) from the external environment. The cell membrane or plasma membrane is a selectively permeable lipid bilayer that encloses the contents of the cell and regulates the transport of materials into and out of it. All cells have a cell membrane that separates the inside and the outside of the cell, and controls what goes in and comes out. As a comparison, human red blood cells, visible via light microscopy, are approximately 8 μm thick, or approximately 1,000 times thicker than a plasma membrane. Web a drawing showing the three main cell membrane components and how they are arranged in a cell membrane. Web by the end of this section, you will be able to: The 3 proteins have lines with the label integral membrane proteins. Web figure 3.2.1 3.2. Web a cell’s plasma membrane defines the boundary of the cell and determines the nature of its contact with the environment. As such, it controls passage of various molecules—including sugars, amino acids, ions, and water—into and out of the cell. On the inner side of the phospholipid bilayer is another protein that is positioned up against the inner portion of the bilayer. Explain the major features and properties of the cell membrane.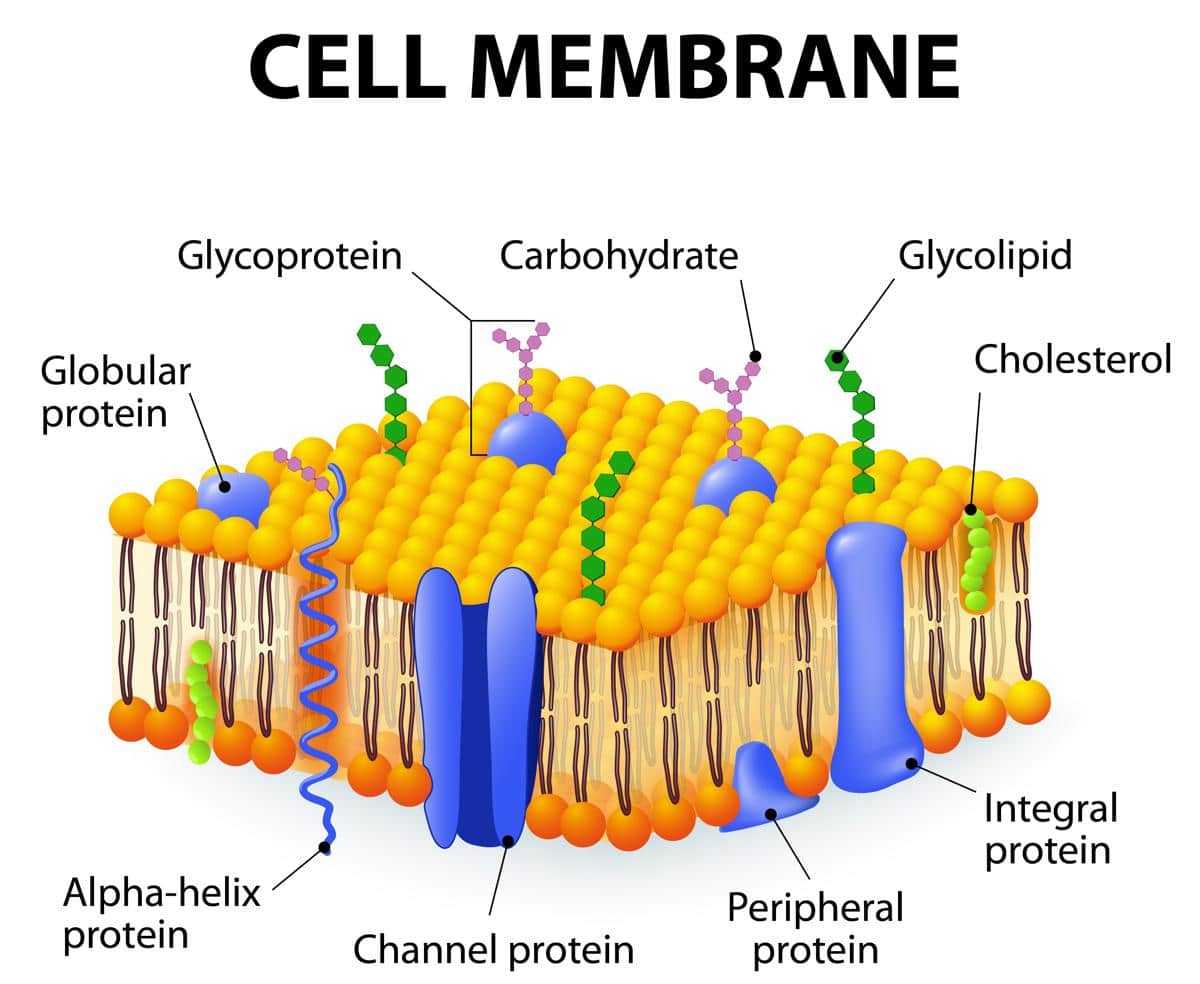
Cell Organelles BIOLOGY JUNCTION
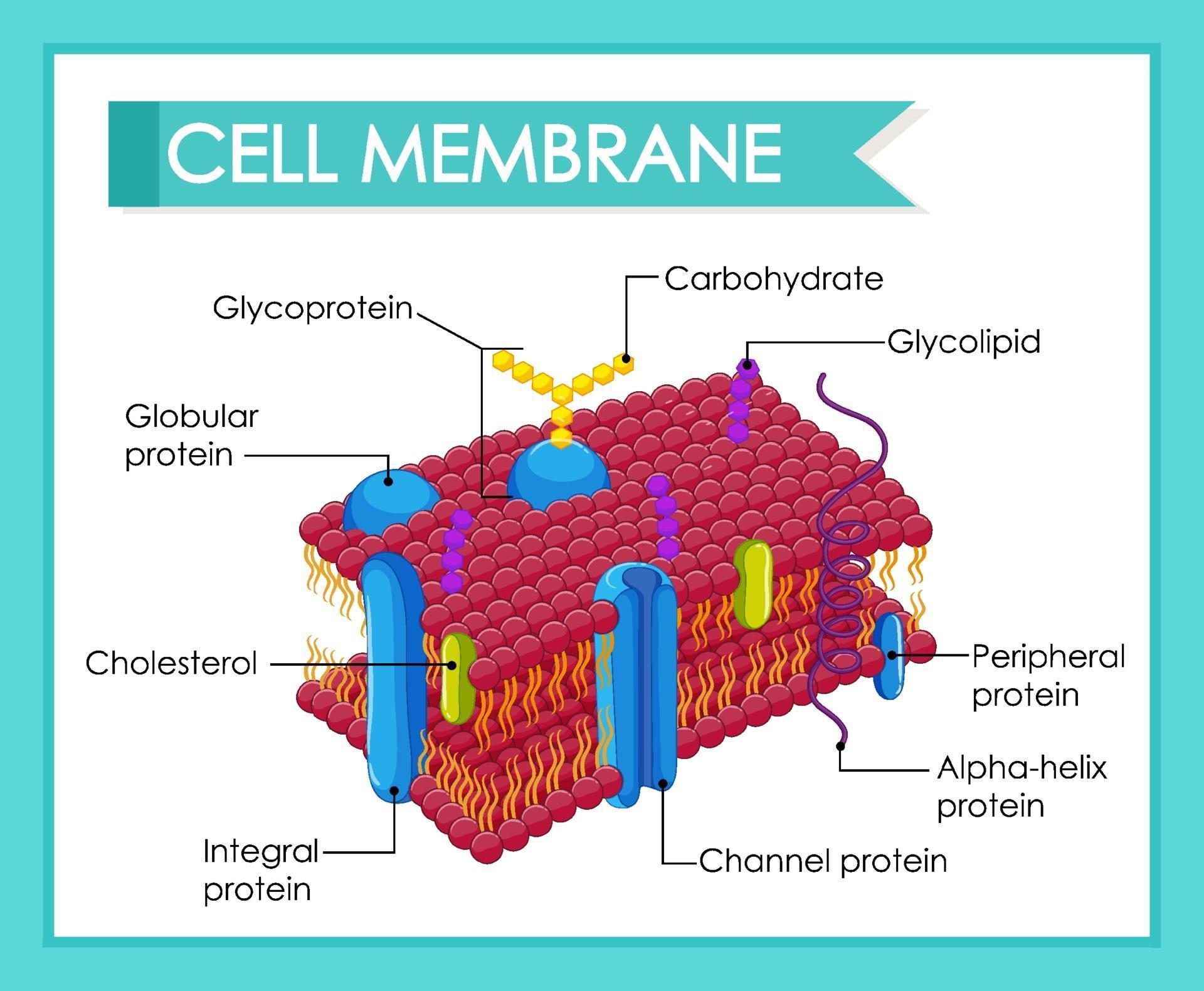
Human cell membrane structure 2053132 Vector Art at Vecteezy
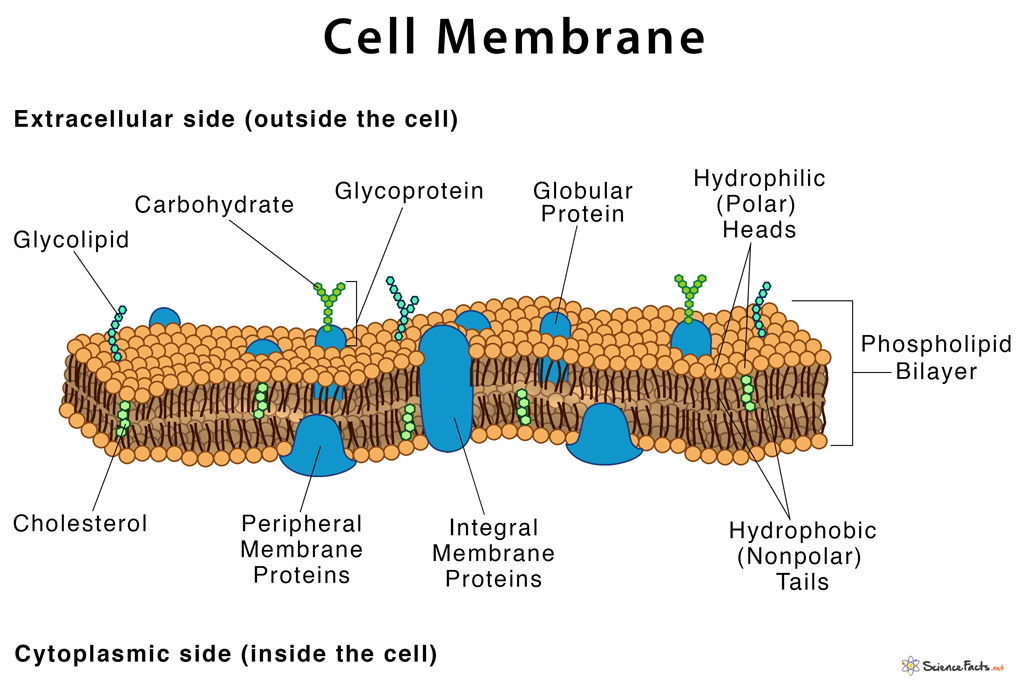
Cell Membrane Definition, Structure, & Functions with Diagram
Web Describe The Structure Of Cell Membranes.
June 6, 2023 By Faith Mokobi.
How Easily These Molecules Can Cross The Membrane Depends On Their Size And Polarity.
A Cell’s Plasma Membrane Defines The Boundary Of The Cell And Determines The Nature Of Its Contact With The Environment.
Related Post: