Cell Division Drawing
Cell Division Drawing - Cells grow and monitor their environment to determine whether they should initiate another round of cell division. Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Typically, mitosis is regulated by certain genes within the body. Mitosis, a key part of the cell cycle, involves a series of stages (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase) that facilitate cell division and genetic information transmission. For cells that will divide again, g 1 is followed by replication of. Cancer and the cell cycle. Phases of the cell cycle. Web mitosis is a process of cell division that helps you stay alive and healthy. In mitosis, the cell replicates all its contents, including eyes, hair, skin, and other muscles. (a) homeostasis parameter β is a function of mechanistic parameters γ and ρ in our model. Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. (a) homeostasis parameter β is a function of mechanistic parameters γ and ρ in our model. For cells that will divide again, g 1 is followed by replication of. Egg or sperm), each with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell. Cytokinesis typically overlaps with anaphase and/or telophase. Phases of the cell cycle. For cells that will divide again, g 1 is followed by replication of. In the first step, called interphase, the dna strand of a chromosome is copied (the dna strand is replicated) and this copied strand is attached to the original strand at a spot called the centromere. Control of the cell cycle. Tabular difference. (a) homeostasis parameter β is a function of mechanistic parameters γ and ρ in our model. Mitosis is a means of asexual reproduction, whereas meiosis is necessary for sexual reproduction. Phases of the cell cycle. Tabular difference between mitosis and meiosis. In other words, in the world of cell biology, mitosis is kind of a big deal! G 1 phase (gap 1 phase) is the first gap, or growth phase in the cell cycle. (a) homeostasis parameter β is a function of mechanistic parameters γ and ρ in our model. I am demonstrating the colorful diagram of mitosis / phases of mitosis (cell. Stages of mitosis in a snap! Web cell division happens when a parent cell divides into two or more cells called daughter cells. Cancer and cell cycle regulation. Egg or sperm), each with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell. Control of the cell cycle. Web mitosis is a process of cell division that helps you stay alive and healthy. Web this image is linked to the following scitable pages: G1 is the period after cell division, and before the start of dna replication. Learn its types, along with the steps and a diagram. Most eukaryotic cells divide in a manner where the ploidy or the number of chromosomes remains the same, except in the case of germ cells where the number of chromosomes is halved. Phase, also called the first gap phase, the cell grows physically larger, copies organelles, and makes the molecular building blocks it will need in later steps. Crossing over, meiosis i, meiosis ii, and genetic variation. 11k views 3 years ago biology diagrams (class 11 & 12) thanks for watching!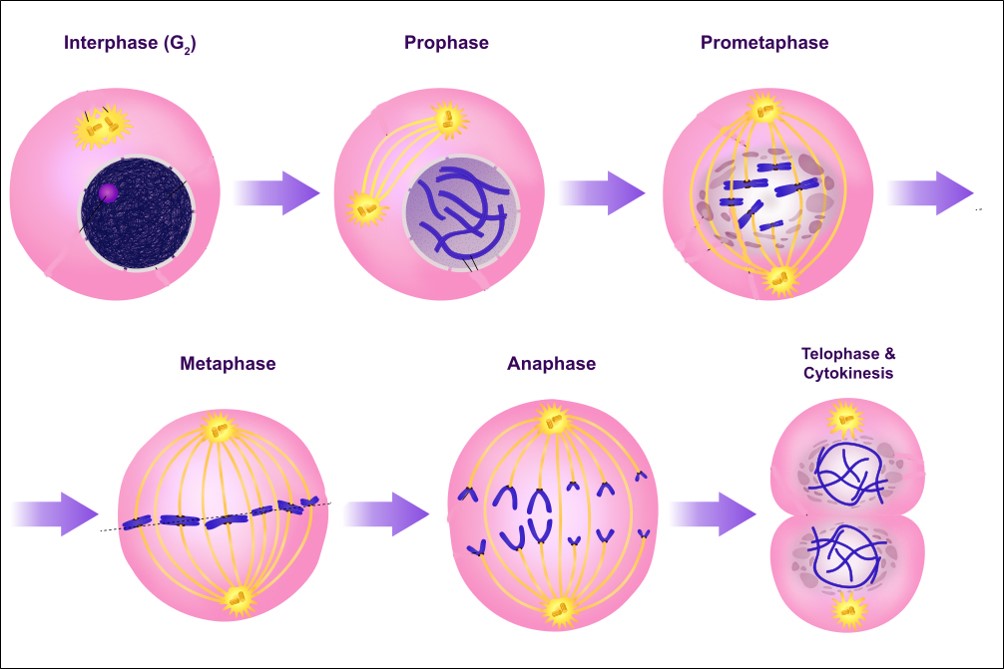
Cell Division Proteins Creative Biomart
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/stages-of-mitosis-373534-V5-5b84992cc9e77c00574f03d3.png)
The Stages of Mitosis and Cell Division
EduPic Cell Drawings
Cytokinesis Typically Overlaps With Anaphase And/Or Telophase.
Cell Cycle And Cell Division.
Web A Cell Grows And Carries Out All Normal Metabolic Functions And Processes In A Period Called G 1 (Figure 3.30).
Mitosis Diagram Showing The Different Stages Of Mitosis.
Related Post: