Calvin Cycle Drawing
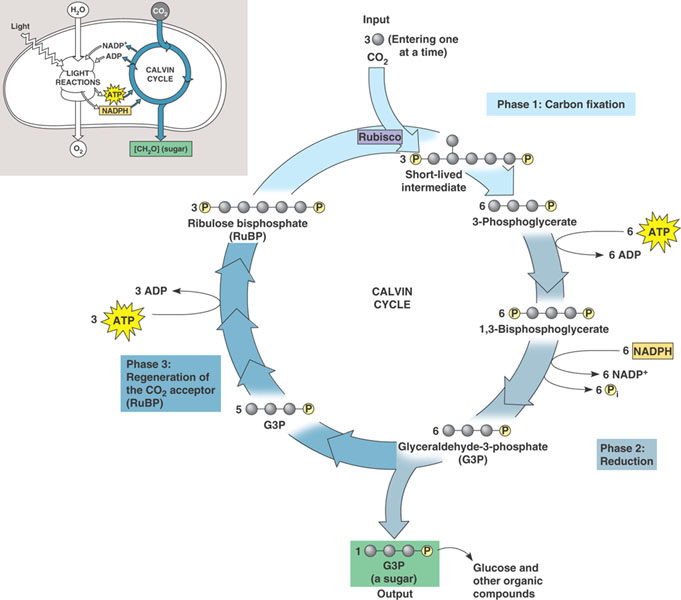
Calvin Cycle Drawing - At this stage of photosynthesis, the energy released from atp produced during light reactions is used to drive the conversion of carbon dioxide and other compounds into an organic molecule (e.g. Web in this article, we will discussion about the stoichiometry of the calvin cycle. Web dark carbon fixation (dcf), through which chemoautotrophs convert inorganic carbon to organic carbon, is recognized as a vital process of global carbon biogeochemical cycle. Web the calvin cycle reactions (figure \(\pageindex{2}\)) can be organized into three basic stages: Web what is the calvin cycle & where does it occur: Web diagram of the calvin cycle, illustrating how the fixation of three carbon dioxide molecules allows one net g3p molecule to be produced (that is, allows one g3p molecule to leave the cycle). Plants use energy from the sun in tiny energy factories called chloroplasts.using chlorophyll in the process of photosynthesis, they convert the sun's energy into storable form in ordered sugar molecules such as glucose.in this way, carbon dioxide from the air and water from the soil in a. What happens during the process, its location, & purpose, explained with steps, example, equation, & simple diagram Web by the end of this tutorial, you should be able to explain what’s going on in the diagram below, which shows the inputs, outputs, and key intermediate compounds of the calvin cycle in a lot more detail. In the stroma, in addition to co 2 , two other chemicals are present to initiate the calvin cycle: These serve as the building blocks for more complex sugars like glucose, starch, and cellulose. Web so far in this series of tutorials, our view of the calvin cycle has involved the diagram shown below (and which you just worked with in the quiz above). Web these molecules store energy for use in the next stage of photosynthesis: Web in. Web the calvin cycle reactions (figure 2) can be organized into three basic stages: Web the travel speed using cycle hires is increased by 1.16 km/h (13.3%), although the effect is insignificant for trips with destinations out of the effect area. At this stage of photosynthesis, the energy released from atp produced during light reactions is used to drive the. However, little is known about the response of dcf processes in estuarine and coastal waters to global warming. Anoxygenic photosynthesis h 2 s 1, 2, 3. In the stroma, in addition to co 2 , two other chemicals are present to initiate the calvin cycle: Web the calvin cycle click on any part of the diagram for more detail. Web. Xiu et al., 2020).the ecological space inside a city. The calvin cycle is a set of biochemical reactions that take place in the chloroplasts of photosynthetic organisms. Stoichiometry is that part of chemistry which deals with the determination of combining proportions or chemical equivalents. Plants use energy from the sun in tiny energy factories called chloroplasts.using chlorophyll in the process of photosynthesis, they convert the sun's energy into storable form in ordered sugar molecules such as glucose.in this way, carbon dioxide from the air and water from the soil in a. With that, plants can rely on these sugars as a structural material. Stages of the calvin cycle. In the stroma, in addition to co 2 , two other molecules are present to initiate the calvin cycle: The calvin cycle has two main stages: An enzyme abbreviated rubisco, and the molecule ribulose bisphosphate (rubp). Web so far in this series of tutorials, our view of the calvin cycle has involved the diagram shown below (and which you just worked with in the quiz above). The calvin cycle is a set of light independent redox reactions that occur during photosynthesis and carbon fixation to convert carbon dioxide into the sugar glucose. Web dark carbon fixation (dcf), through which chemoautotrophs convert inorganic carbon to organic carbon, is recognized as a vital process of global carbon biogeochemical cycle. Web the calvin cycle reactions (figure \(\pageindex{2}\)) can be organized into three basic stages: Web the calvin cycle reactions (figure 5.15) can be organized into three basic stages: Web the calvin cycle reactions (figure 2) can be organized into three basic stages: Web what is the calvin cycle & where does it occur:
Calvin Cycle (Dark Reaction) — Equation & Steps Expii
Calvin Cycle Biology Resource
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/2000px-Calvin-cycle4.svg-58a397c25f9b58819c5ba0d6.png)
Diagram and Explanation of the Calvin Cycle
An Enzyme Abbreviated Rubisco, And The Molecule Ribulose Bisphosphate (Rubp).
It's The Second Major Stage In Photosynthesis Where The Plant Uses Energy From The Sun To Convert Carbon Dioxide Into Glucose.
Web The Calvin Cycle Reactions (Figure \(\Pageindex{2}\)) Can Be Organized Into Three Basic Stages:
Web By The End Of This Tutorial, You Should Be Able To Explain What’s Going On In The Diagram Below, Which Shows The Inputs, Outputs, And Key Intermediate Compounds Of The Calvin Cycle In A Lot More Detail.
Related Post: